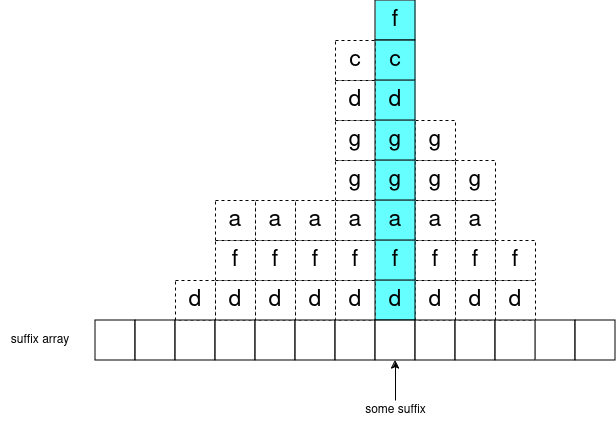
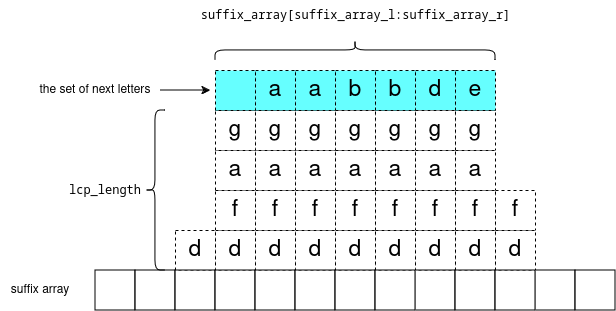
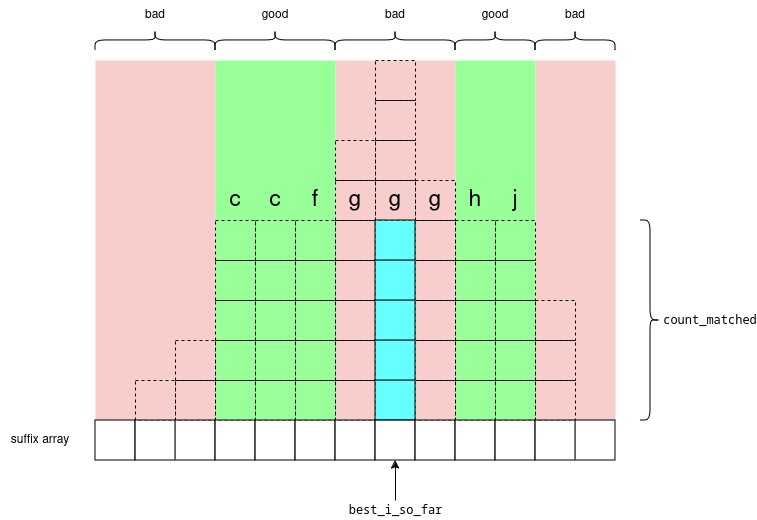
For the longest time, this comment https://codeforces.me/blog/entry/112755#comment-1004966 was bugging me (the part about how the 'complete' segment tree is 20% slower (complete, because it’s a complete binary tree)). Instead of benchmarking, this blog calculates the expected number of recursive calls visited between segment tree implementations.
Thanks to camc for giving valuable feedback.
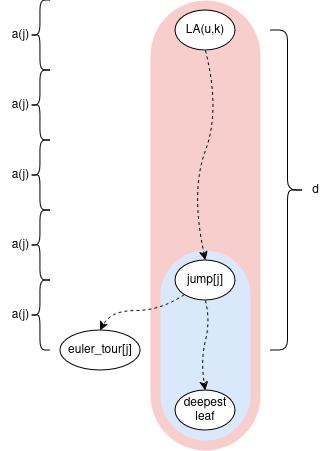
This blog will study 2 implementations of segment trees.
And
(complete, because it’s a complete binary tree); Also tourist uses the iterative version of this.
Structure
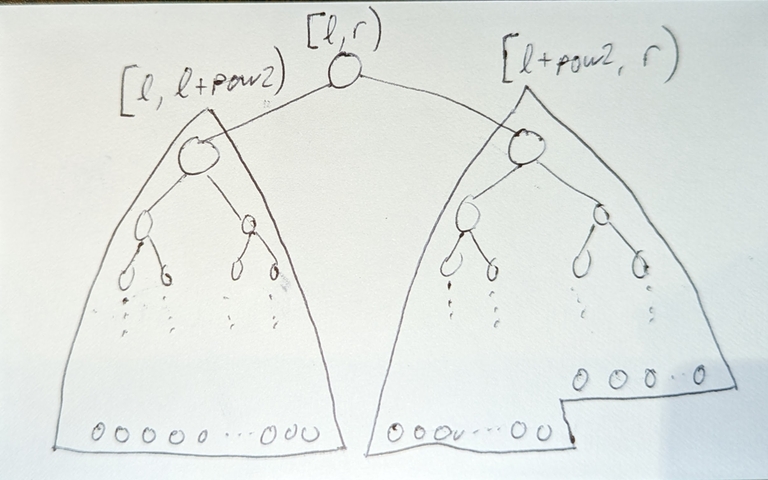
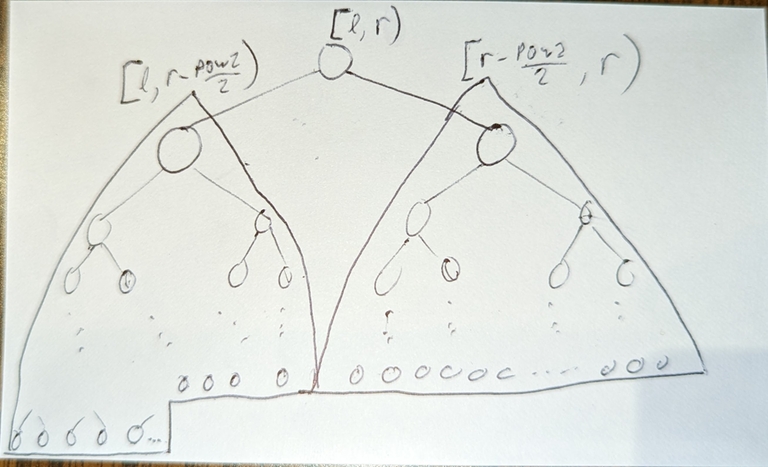
Consider the structures of 'standard' segment trees on n=1,2,3,...
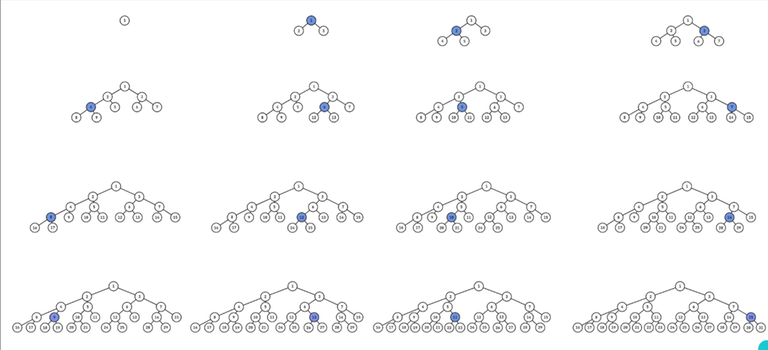
(credit to this tool for making the pictures; here are the pictures in higher resolution)
Notice going from one tree to the next, exactly one leaf node turns into an internal node, and “grows” 2 new leaves. Well consider the sequence of the nodes which “grow” 2 new leaves:
1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 5, 7, 8, 12, 10, 14, 9, 13, 11, 15, …
It is exactly this sequence https://oeis.org/A059893. But this sequence is about reversing bits, so how is it related?
As you increment n, the child (left or right) of the root whose range-size increments will alternate (so it’s based on parity/LSB of n), then the child’s range-size is half of the root’s range-size and you repeat to determine which grandchild’s range-size increments (it also alternates), and so on. Eventually you get to a leaf, and this leaf’s range-size increments (i.e. “grows” 2 new leaves).
If you split up the sequence into subarrays [1,2), [2,4), [4,8), ..., [2^(i-1),2^i),..., then:
- the
i-th subarray represents all nodes at depthi - Every node at depth
igrows its leaves before all nodes at depth(i+1), and after all nodes at depth(i-1) - So as n increases, the standard segment tree grows its leaves layer by layer, i.e. each layer is completed fully before the next layer’s leaves start growing.
abs(depth(leaf_i)-depth(leaf_j))<=1for any pairs of leaves
Point updates/queries
Expected number of recursive calls of point update
= expected depth of leaf node (where depth of root=1)
= sum_of_leaf_depths/n
So how to work out the sum of depths of leaves?
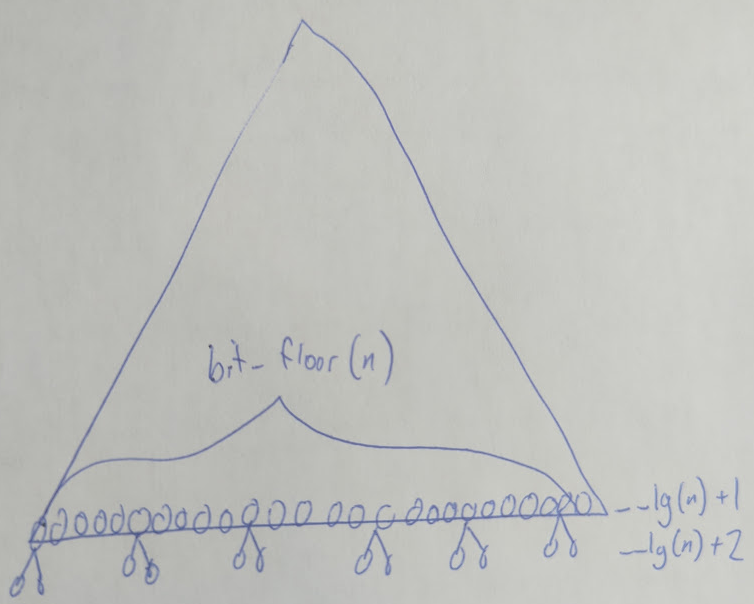
Well there are x leaves of depth __lg(n)+1 and y leaves of depth __lg(n)+2. We have:
x+y=ny = 2*(bit_floor(n)-x)because there arebit_floor(n)-xinternal nodes at depth__lg(n)+1, each having 2 leaf-childs.
Then sum of depths of leaves = x*(__lg(n)+1)+y*(__lg(n)+2).
Finally notice, this math is exactly the same for both the complete segment tree and the standard segment tree, so they have the same sum of leaf depths.
Also for merge sort tree: (sum of array lengths) = (sum of leaf depths). So the respective merge sort tree’s have the same sum of array lengths.
Range updates/queries
Expected number of recursive calls of range update
= total_recursive_calls_over_all_possible_updates/(n*(n+1)/2)
I was blown away by this. I thought that the complete segment tree should have more recursive calls because the ranges aren’t split in the middle. But somehow this is wrong? Let’s see why.
I was able to come up with this formula for the total number of recursive calls (derivation left to the reader haha).
Comparing this formula for complete versus standard segment tree:
(-7n^2-3n+4)/2is the same- sum of
[depth*(2n+3)]over leaves is the same as they both have the same number of leaves at depths__lg(n)+1and__lg(n)+2
The only difference is we subtract f(n) = n^2 + f(left child range-size) + f(right child range-size) from the total number of calls. And f(n) increases when abs(left child range-size - right child range-size) increases, i.e. as the tree becomes less balanced.

To me, this result is unintuitive. I’d be interested if anyone can come up with some intuition for this.
But then why is the complete segment tree slower...
Calculating the midpoint has a larger constant.
- https://judge.yosupo.jp/submission/270739 288 ms 15.82 Mib — complete segment tree
- https://judge.yosupo.jp/submission/270737 298 ms 16.27 Mib — standard segment tree, but with artificially inflated constant factor of calculating midpoint