Let's discuss problems.
How to solve A, D, G, J?
| № | Пользователь | Рейтинг |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | tourist | 3993 |
| 2 | jiangly | 3743 |
| 3 | orzdevinwang | 3707 |
| 4 | Radewoosh | 3627 |
| 5 | jqdai0815 | 3620 |
| 6 | Benq | 3564 |
| 7 | Kevin114514 | 3443 |
| 8 | ksun48 | 3434 |
| 9 | Rewinding | 3397 |
| 10 | Um_nik | 3396 |
| Страны | Города | Организации | Всё → |
| № | Пользователь | Вклад |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | cry | 167 |
| 2 | Um_nik | 163 |
| 3 | maomao90 | 162 |
| 3 | atcoder_official | 162 |
| 5 | adamant | 159 |
| 6 | -is-this-fft- | 158 |
| 7 | awoo | 155 |
| 8 | TheScrasse | 154 |
| 9 | Dominater069 | 153 |
| 10 | nor | 152 |
Let's discuss problems.
How to solve A, D, G, J?
| Название |
|---|



J: check on a lot of random modules <= 5000.
UPD: oops, my solution is wrong
If the given number is divisible by every number up to 5000, this will fail. To make it pass, we have to increase the upper limit.
Different tests (33-52) contain integers divisible by every prime up to 107, and tests 33-34 are divisible by all primes from 2 to 833 947 simultaneously.
Seems that there were no tests with given number divisible by every number up to 5000 because i have an OK
Yeah, taking larger powers of very small primes as witnesses can pass these tests.
Anyway, as with hashing, there sure are tests against every possible small collection of witnesses known in advance, but there is no known test against every possible witness, so it's normal for such solution to pass, except if it chooses only few small and fixed primes.
J:
We solve it by Euler's criterion. Pick about K primes, module the given integer and test it with Euler's criterion. The probability of failure will be about 2 - K.
Thank you. Finally got AC with first 50 prime numbers bigger than 109 + 7.
G (div.2: up to 4*N moves):
Stand with knight in the same column, next stand in the same row. Now you are very close to him.
Then on every move try to stay in the same row as knight do, but slightly go to the right if the knight is on the right, otherwise slightly go to the left. Later means to go diagonally.
You don't need to read size of board or check borders, because you go only where the knight proved the board exists.
Is that all that you do? It seems that I can last for more then N turns this way
Suppose N = 2K — big enough
Queen=(1, 1);Knight = (K, N)
Turn1: Queen=(K, 1), Knight = (K+2, N — 1)
Turn2: Queen=(K, N — 1). Knight = (K + 1, N — 3)
Now I think you need 2N — 1 more turns to win And it will be even a bit more, if we move knight starting point to the left to (2,N) or so
(column first in all coordinates)
For N it is not enough. Div.2 problem statement is: to not exceed 4*N moves (
"Your task is to capture the Knight in at most 4N moves"). No access to Div.1 statement. My solution works in 2*N I think.For Div1 it is at most N moves.
I think your solution is 2N+1 moves
We used basically the same idea(go to the same row, then win in O(2 * halfwidth), but we needed additional bruteforce for first few turns because otherwise sometimes we needed N + 1 turns
How to solve B, H?
H is the computation of a resultant (case t = xy in https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Resultant#Number_theory ), but general algorithms for computing resultants are not fast enough. It seems that an efficient algorithm is given in http://algo.inria.fr/flajolet/Publications/BoFlSaSc02.pdf (Corollary 4).
H:
Using this one can easily find the k-th coefficient of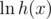 and then calculate
and then calculate 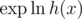 .
.
I am not sure if I understand how to use this equation
So we calculate all logarithms (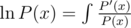 ), calculate
), calculate 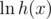 from the logarithms of f and g and calculate the exponent.
from the logarithms of f and g and calculate the exponent.
B is similar to Jigsaw Puzzle from Moscow Subregional 2013.
We can solve it with dp by profile. State is:
column id
mask of colors in last column
list of possible masks (each mask: has 1 on position i if there is a horizontal pile from last column to next one in row i)
Yes, it looks like m * 2^n * 2^(2^n) states. But most of states are unreachable. And for n=6 there are about 1600 reachable states per column.
B. Checking if coloring is good can be done by dynamic programming on set of border points which are already colored. Dynamic programming of set of states reachable states of dynamic programming above on one layer works fast enough to pass or precalc (~1.2s in yandex context for me).
See code for more details. I think it's quite easy.
Can you please explain meaning of a few things: mask, x.first, the for loop inside go (what does the i stand for)?
Edit: I think I understood the gist.
Mask: colors of previous column (not exactly previous column, if you are at r,c then they represent colors of cells i,c for i<r and I,c-1 for i>=r)
x.first: every bit represents status of the previous column (not exactly, defined as above). 0 means not yet covered and 1 means already covered.
Loop I: for each of the covered/uncovered status we try to figure out if we want to color current cell bit then what are the possible next statuses.
Yes, you are correct. Probably naming could be a bit more understandable :)
It took me 140 minutes to solve 7 tasks and more than 3 hours to solve H, I feel this is an overkill, but anyway...
We use Newton's identities. Check the definitions of ei and pi there.
Let A = {ai}, B = {bi}, C = {aibj}. We are given the values of ei(A) and ei(B), and we want to get ei(C).
Thus, the main challenge is the conversion between pi and ei.
Now, let's use Newton's identities. It says that the convolution of (0, p1, - p2, p3, - p4, p5, - p6, ...) and (e0, e1, e2, ...) is (0, e1, 2e2, 3e3, 4e4, ...). Let P(X) = 0 + p1X - p2X2 + p3X3 - p4X4 + ... and E(X) = e0 + e1X + e2X2 + e3X3 + .... We have P(X)E(X) = E'(X)X (Don't miss derivative sign).
The conversions between P and E can be done as follows:
Computation of inverses: Link (Check problem E)
Computation of exponentiation: Link (Left part of Fig.1 is enough)
(I'm not quite sure why these computations with integrations/differentiations are valid.)
Yes, it's exactly the author's solution. When I was preparing this problem, I first came up with the idea to use Newton's identities to convert between ei and pi. After a while, I realized, that this could be done efficiently using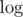 and
and 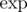 .
.
So I decided to use this big constraints in the problem statement, so that more obvious solutions don't pass. If the constraints were smaller, one could use Berlekamp's algorithm or Cantor–Zassenhaus algorithm to factorize the polynomials, and after that just multiply a lot of linear polynomials.
Your solution and Golovanov399's solution are the same, by the way.
You can calculate log and exp efficiently using Newton's method.
Also, you should notice, that log and exp are not well-defined when we are working modulo 998 244 353, because we sometimes divide by zero. But we don't need that. We are only interested in the first 105 coefficients of polynomials, so log and exp are well-defined.
Conversion between pi and ei could be done by divide-and-conquer FFT.
We solved H by Newton-Girard formulas and divide-and-conquer FFT.
D: first bring the outter point to the inner layer in the shortest possible way. Then continue descending in the same manner, checking whether it’s optimal to traverse the current layer to connect the two points :)
For problem A, first consider the same problem on a square grid. It can be easily shown that, if we fix the perimeter, a polyline with the largest area is the polyline most closely resembling a square: the sides are either all equal or differ by 1.
On a hexagonal grid, the reasoning is similar, although there happen to be more cases. Sure, our wall will be a convex hexagon. We can show that two consecutive sides differ by at most two: otherwise, we can get a larger area with the same perimeter. In Figure 1 below, we change the part ABC of the wall with lengths 2 and 5 to part DEF, increasing the total enclosed area by 1 (the difference is that we get XEFC instead of DABX).
Thus we can take a rough guess of what will be the length of one side s, then try all values from s - 2 to s + 2 for the two neighboring sides, and so on.
If we investigate further a bit, we can find the optimal solution for each possible perimeter. The six cases are shown on Figure 2 below.
Here is a short solution summarizing the six cases.
A piece of hexagonal paper was provided in the statement to help solve the problem.