This is a technical problem. You should do exactly what is written in problem statement.
600B - Queries about less or equal elements
Let's sort all numbers in a. Now let's iterate over elements of b and for element bj find the index of lowest number that is greater than bj. We can do that using binary search. That index will be the answer for value bj.
Complexity: O(nlogn).
Let's denote cntc — the number of occurences of symbol c. Let's consider odd values cntc. Palindrome can not contain more than one symbol c with odd cntc. Let's denote symbols with odd cntc as a1, a2...ak (in alphabetical order). Let's replace any one of symbols ak with symbol a1, ak - 1 with a2 and so on until the middle of a. Now we have no more than one odd symbol. If we have some let's place it in the middle of the answer. First half of answer will contain 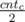 occurences of symbol c in alphabetical order. The second half will contain the same symbols in reverse order. For example for string s = aabcd at first we will replace d by
occurences of symbol c in alphabetical order. The second half will contain the same symbols in reverse order. For example for string s = aabcd at first we will replace d by
Unable to parse markup [type=CF_TEX]
in the middle and after permuting the symbols we got abcba. Easy to see that it's the optimal solution.Compexity: O(n).
600D - Area of Two Circles' Intersection
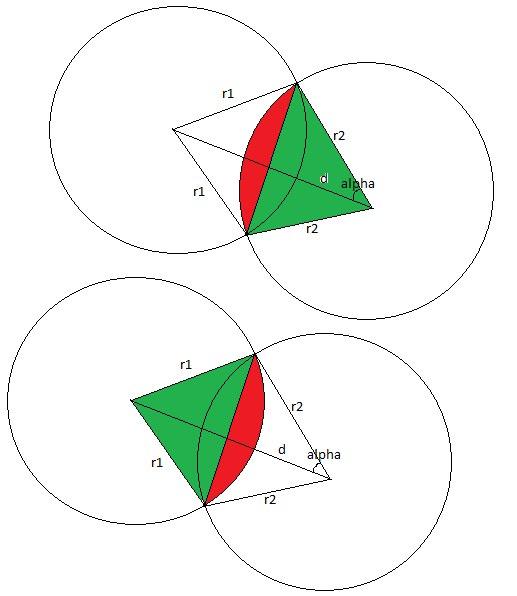
If the circles don't intersect than the answer is 0. We can check that case with only integer calculations (simply by comparing the square of distance between centers with square of the sum of radiuses). If one of the circles is fully in other then the answer is the square of the smaller one. We can check this case also with only integer calculations (simply by comparing the square of distance between centers with square of the difference of radiuses).
So now let's consider the general case. The answer will be equal to the sum of two circular segments. Let's consider the triangle with apexes in centers if circles and in some intersecting point of the circles. In that triangle we know all three sides so we can compute the angle of the circular segment. So we can compute the square of circular sector. And the only thing that we should do now is to subtract the square of triangle with apexes in the center of circle and in the intersecting points of circles. We can do that by computing the half of absolute value of cross product. So we have the following formulas:
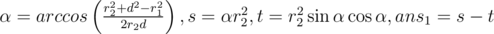 ,
,
where d is the distance between centers of the circles. And also we should do the same thing with second circle by replacing of indices 1 ≤ ftrightarrow2.
Complexity: O(1).
The name of this problem is anagram for Small to large''. There is a reason for that :-) The author solution for this problem uses the classic technique for computing sets in tree. The simple solution is the following: let's find for each vertex <span class="tex-span"><i>v</i></span> themap<int, int>'' — the number of occurences for each colour, set<pair<int, int>>'' — pairs the number of occurences and the colour, and the number <span class="tex-span"><i>sum</i></span> — the sum of most frequent colours in subtree of <span class="tex-span"><i>v</i></span>. To find that firstly we should find the same thing for all childs of <span class="tex-span"><i>v</i></span> and then merge them to one. These solution is correct but too slow (it works in <span class="tex-span"><i>O</i>(<i>n</i><sup class="upper-index">2</sup><i>logn</i>)</span> time). Let's improve that solution: every time when we want to merge two <span class="tex-span"><i>map</i></span>-s <span class="tex-span"><i>a</i></span> and <span class="tex-span"><i>b</i></span> let's merge the smaller one to larger simply by iterating over all elements of the smaller one (this is theSmall to large''). Let's consider some vertex v: every time when vertex v will be moved from one map to another the size of the new map will be at least two times larger. So each vertex can be moved not over than logn times. Each moving can be done in O(logn) time. If we accumulate that values by all vertices then we get the complexity O(nlog2n).
I saw the solutions that differs from author's but this technique can be used in a lot of other problems.







