1043D - Mysterious Crime requires you to input 1 million integers and ultimately process them in either nm or 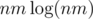 time. But the time limit was set to only 1 second. This is very unfriendly to any language that isn't C++, and it even puts
time. But the time limit was set to only 1 second. This is very unfriendly to any language that isn't C++, and it even puts 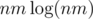 C++ solutions at risk of failing.
C++ solutions at risk of failing.
Case in point: tourist's contest submission uses an STL map and exceeded the time limit, causing him to drop over 100 places. Meanwhile, ksun48 and mnbvmar had almost exactly the same solution and barely squeezed by the time limit in 998 ms. tourist was also able to pass with the same code in practice mode by switching from C++11 to C++14, which shows how close it was.
I admit there are certain problems where it is interesting to distinguish O(n) and 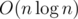 solutions, but this doesn't fit that case, as it doesn't take any novel insight to remove the log from the runtime here. Overall it would have been much better with a time limit of 2 or 3 seconds; or alternatively, with m ≤ 5 instead of 10.
solutions, but this doesn't fit that case, as it doesn't take any novel insight to remove the log from the runtime here. Overall it would have been much better with a time limit of 2 or 3 seconds; or alternatively, with m ≤ 5 instead of 10.











To be clear, I believe the problem setters most likely weren't aware of the map solution, and I don't want to blame anyone in particular. But in general I've been observing a lot of strict time limits on problems where more lenient limits would be better.
What's makes this problem worse is that my map solution showed only around 500ms for pretests :( It may be my fault for not knowing that 10^6 map operations wouldn't pass in 1s, but couldn't the pretests be stronger?
I had a nmlogn solution and it worked the same on pretests and systests (about 500 ms). Seems that you just can't put maxtest for every solution in there.
I'm kinda surprised about C++ people having problems with the time limit on D as it was very much solveable in python (pypy only took 421 ms for me). Problem E on the other hand might be impossible in pypy as the I/O is simply too big relative to the time limit.
I think has more to do with STL map<> in particularly performing poorly with integers pairs than with C++ performance in general.
No, the problem was that with pairs you use O(3*n*m) integers + pointers that might be used in the map structure + extra stuff needed in the map structure (for tree rebalancing for example) + realocations inside map + lots of cache misses. If you remove the map and use vector + sort it'll probably pass way faster.
Yeah I didn't elaborate. Set and Map have horrible constant factor because not cache friendly like vector. When you have all the extra stuff in integer pairs it is even worse.
Challenge accepted — 45036971
Ah so it was possible. In my code I usually use input = sys.stdin.readline but switching to input = iter(sys.stdin.read().splitlines()).next made it run in 1.5 s. Haven't seen that one before, it is a nice combination between reading all input at one time and still having the functionality of the usual input. Using some homemade string to int conversion I was even able to get it to 1.3 s. Will remember this for the future, thanks!
Indeed, looked through your solutions, didn't strike me to use a custom-made str to int and consider the input file as an array, I think that's a great way to get better computation speed. (Especially since Python's builtin str to int is slow).
After playing around with this for a while I've noticed that input = iter(sys.stdin.readlines()).next seems to be a bit better than iter(sys.stdin.read().splitlines()).next . Also I've pretty much only seen improvements using this over input = sys.stdin.readline. For example on this problem my solution went from taking 951 ms down to 327 ms. I will definitely use this in the future for pretty much every problem I solve.
Thanks! I have more optimizations I've tinkered with here that might interest you too.
It's also notable that both ksun48 and mnbvmar used C++17 in contest, while (as mentioned in blog) tourist used C++11. When he submitted in C++14 it passed much more comfortably. Especially considering that there is some fluctuation in running times on codeforce judge, I think that especially for these problems (where 2000ms will still eliminate naive solutions) adding on more TL can't really hurt the competition and makes it more about solving problems than choosing the latest version of C++
Why is an inefficient solution failing something bad? This isn't about distinguishing solutions — with one extra log, you often can't do that anyway. As a contestant, when you see 1 million as a constraint, you may want to think about a linear-time solution or weigh your chances, think if your idea with log will work in time, maybe use custom test to check and decide what to do based on the specific situation. A tighter limit simply means "we're fine with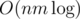 solutions passing if they're well-written, but we're not going to put extra effort into making sure they all pass". Note that 1 second is a default TL in Polygon.
solutions passing if they're well-written, but we're not going to put extra effort into making sure they all pass". Note that 1 second is a default TL in Polygon.
I think having such a solution fail is sometimes ok, but if you are going to do that you should at least let people know that it is going to fail (by for example putting a maxtest in pretests) instead of having it pass pretest in like half the TL and then suddenly fail in systest
Did the setters even think about such a slow solution though? Again, 1 second is default TL, it doesn't have to be specifically set with these solutions in mind. Also this.
Yeah, I suppose it's really hard to prevent something like this from happening if the authors don't think of the solution
I think it's fine if the TL is even tighter and all solutions with log factors fail. It's also fine if the TL is looser and allow all solutions with log factors. But something in the middle should be avoided, whenever possible (in this case a constant-optimization technique can be a decisive factor).
If the TL is tighter, then constant optimisation can be a decisive factor for linear solutions (or rather writing a solution that isn't constant-inefficient). As a problemsetter, I would rather risk making luck (or skill at constant optimisation) a bigger factor for asymptotically suboptimal solutions than for asymptotically optimal.
I think if you solved it with map, you solved it wrong. I solved in O(nm) using dsu
DSU sounds really cool bro. How about just using for loop?
After the contest I submitted my code that got TL 36 and get AC. Identical codes(even compilers are the same):
http://codeforces.me/contest/1043/submission/45016350
http://codeforces.me/contest/1043/submission/45031166
Even tmwilliamlin168's solution got AC :\
Actually, I used c++14 http://codeforces.me/contest/1043/submission/45002137 during the contest :'(
Edit: my solution also passes now with c++14 http://codeforces.me/contest/1043/submission/45031725
But, I used c++17 :(
That's because the CF judge will run solutions that are very close to the TL multiple times I think.
NO, i once got a tle on a pretest in systesting.And also same code with same compiler can get accepted after the contest if it's worst case running time is close to time limit.
Isn't that what I am saying?
If, during a contest, your solution runs in very close to TL, CF will run it multiple times. If it goes over the TL even once, I guess it will TLE.
In contrast to when you submit it manually, where whether or not it passes in TL could be completely a matter of luck (997 vs 1000ms is not a huge difference) as it is run only once.
Yes sorry.. apparently i am neither reading comments nor problem statements correctly these days..
Agreed! I think the problem-writing philosophy should be to set the loosest constraints that keep out undesired complexities instead of setting the tightest constraints that allow good complexities. The naive here is O(N2M), far from workable (and even an optimized O(N2) is unlikely to come close). In general, I'd argue for allowing the occasional hyper-optimized naive to sneak through over allowing correct solutions to fail.
Related side-note: I'm a little sad that fast I/O is becoming a requirement for many of the problems on CF. For veterans it's just a matter of adding two lines to template, but it increases the barrier to entry for newer contestants and punishes lots of solutions that deserve to pass.
“But it increases the barrier to entry for newer contestants”
Very cool seeing a nutella that has empathy with begginers. Maybe you could teach Um_nik?
(just kidding :)
So empathy with beginners is about allowing them do what they want and telling that they are good anyways? You used slow I/O but that's okay, we raised TL for you. You can't read but that's okay, you always can ask authors to explain problem just for you. Maybe we should also tolerate those using python and set limitations such that only 1e7 operations fit in 1 second?
Imagine your teachers giving you A for anything. Would you learn anything? Don't think so.
No. But I would still be getting an A.
So let's give rounds consisting of one A+B problem. Everyone is a winner!
As someone who's used to squeezing in stupid sqrt-solutions for problems that are otherwise pretty hard, I should support this...
My recommendation for setting TLs:
Of course, sometimes it's impossible to satisfy the rules above. In such cases maybe we should admit that some poorly-written solutions may fail. But when the difference between good solutions and bad solutions is clear, I follow the rules above.
Why not to use unordered_map instead of map here ??
Mostly because
unordered_mapcan be hacked (without the proper adjustments).Why not just use an array instead of unordered_map? The indexes are up to 105 anyway.
Even O(n*m) failed for me — http://codeforces.me/contest/1043/submission/45070910
BTW, MS C++ is ok in 700ms.
Yes, this is unfortunately because you need to add the following two lines to the beginning of your program for faster cin/cout (something scott_wu mentioned above):
Why simple didn't put time limit 2s for all normal problems, and more than 2s for hardest problems?? ~1s for I/O, and 1s for solution.
And, may be stop to play between with 10^5, 2*10^5, 3*10^5, 4*10^5, 10^6 for limit of N, also. =).
I'm not saying that CF doesn't need to loosen its time limits a bit, but just to clear things up a bit: 1043D had an O(NM) solution, passing without any issues.
Yes, I say all this as someone who implemented the O(nm) solution during the contest: 45003278. My code uses about 1/4 of the available time, and I still think the time limit should be adjusted so that the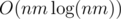 solution passes comfortably.
solution passes comfortably.
What if someone used more insertions into map<> (e.g. 3x more) and complained about the time limit not allowing his solution, but allowing some with the same complexity that just insert fewer times?
At some point there will be a high enough constant factor on an appropriate-complexity solution that you cannot distinguish well from a hyper-optimized, but worse-complexity solution.
So I am not saying you can always get it perfect, but you can definitely think about where to set the cutoff and try to make it relatively lenient. My main point is that for this problem (and several others), the constraints are much higher and the time limit much stricter than necessary.
I agree with the general principle, but I don't think it was strict. My in-contest linear solution runs in 185 ms and http://codeforces.me/blog/entry/62808?#comment-467989 is a solution with log that runs in 500 ms. If you put 1 million pairs into map<> and get TLE because map is slow, that doesn't make the TL strict.