221A - Маленький Слоник и функция
В этой задаче все что нужно заметить это то, что ответ всегда имеет следующею форму: n, 1, 2, 3, ..., n-1. При такой перестановке не трудно заметить, что после полого выполнения алгоритма перестановка будет отсортирована.
221B - Маленький Слоник и числа
Нужно найти все делители числа n. Это можно сделать простым перебором от 1 до sqrt(n). После этого нужно написать функцию, которая умеет определять, существуют ли две одинаковые цифры в паре чисел. Это тоже можно сделать простым перебором по цифрам.
220A - Маленький Слоник и проблема
Существует несколько решений этой задачи. Например, можно найти максимальное x такое, что существует y (минимальное возможное) такое, что (y < x) и Ax < Ay. После этого остается проверить ровно два варианты — либо менять местами x-е и y-е числа, либо не делать ничего.
220B - Маленький Слоник и массив
Задачу можно решить за O(NsqrtN), но я опишу решение за O(NlogN).
Будем решать задачу в оффлайне, тоесть сначала считаем все запросы, а потом будем давать ответы. Для каждого x (0 ≤ x n) мы должны держать все запросы, концами которых есть x. Будем перебирать x от 0 до n - 1. Также нам нужно поддерживать массив чисел D такой, что для текущего x ответом на запрос [l;x] будет число Dl + Dl + 1 + ... + Dr. Для правильной поддержки массива, перед тем как обрабатывать запросы для текущего x, нудно обновить D. Пусть t — текущее число, тоесть Ax, а вектор P — список индексов всех вхождений числа t (до позиции x), нумерация с 0. Тогда, если |P| ≥ t, нам нужно добавить 1 до DP[|P| - t], так как эта позиция теперь переломной — после нее будет не меньше чем t вхождений числа t. Потом, если |P| > t, нужно отнять 2 от DP[|P| - t - 1], для того что-бы закрыть текущий интервал (после этой позиции количество вхождений t будет превосходить t), а также отменить предыдущий. И наконец, если |P| > t + 1, нужно еще добавить 1 к DP[|P| - t - 2] для того что-бы отменить закрытие предыдущего интервала.
220C - Маленький Слоник и сдвиги
Each of the shifts can be divided into two parts — the right (the one that starts from occurrence 1) and the left (the rest of the elements). If we could keep minimal distance for each part, the minimal of these numbers will be the answers for the corresponding shift. Lets solve the problems of the right part, the left will be almost the same.
Let we have some shift, for example 34567[12] and the permutation A is 4312765 and B is 2145673, then shifted B is 4567321. Let we keep two sets (S1 and S2). The first will keep all the distances from integers in current left part to the corresponding positions in A (for the example above, it is [2, 4]). When you come to the next shift, all integers in S1 should be decreased by 1 (that is because all distances are also decreased by 1). But now some integers in set may be negative, when any negative integer occures (it always will be -1) you need to delete it from S1 and put 1 to the S2. Also after shifting to the next shifts, all integers in S2 must be increase by 1. After that, for any shift, the answer will be minimum from the smallest numbers in S1 and S2.
It was very useful to use standart "set" in C++.
220D - Маленький Слоник и треугольник
Давайте переберем все возможные точки нашей плоскости и предположим что это первая точка тройки. Пусть это будет точка (x;y). Пусть вторая и третья точки это (x1;y1) и (x2;y2). Тогда удвоенная площадь равна |(x1 - x)(y2 - y) - (x2 - x)(y1 - y)|. Нам нужно что-бы это число было четным, а также ненулевым. Для начала найдем количество троек, которые образуют четную площадь, а потом отнимем количество точек с нулевой площадью.
Первая подзадача. Так как мы знаем x и y и нам нужно проверить четность, давайте еще переберем все возможные 24 варианты четности x1, y1, x2 и y2 (пусть это d0, d1, d2 и d3, соответственно). Потом проверим будет ли такая тройка чисел формировать 0 после подстановки в формулу площади и взятии по модулю 2. Если это так, тогда нужно добавит к ответу число cxd0cyd1cxd2cyd3, где cxd равно количеству целых чисел в промежутке [0..n] таких, что они по модулю 2 равны d. Аналогично для cyd, только в промежутке [0..m].
Теперь нужно отнять плохие тройки — такие, что треугольник, который они создают, имеет нулевую площадь. Это значит, что тройка точек формирует отрезок (или точку). Так как это отрезок, давайте переберем dx = |x1 - x2| и dy = |y1 - y2|, вместо перебора всех 4 координат. Количество таких отрезков на плоскости равно (n - dx + 1)(m - dy + 1). Также для подсчета количества троек, что формируют такой отрезок, нужно искать количество точек с целыми координатами на плоскости, которые лежат на этом отрезке. Это известная задача — это количество равно gcd(dx, dy) + 1.
Это дает нам, с еще некоторыми оптимизациями, решение за O(nm).
220E - Маленький Слоник, а также инверсии
В этой задачи нужно использовать метод двух указателей. Также нужно использовать RMQ. Если вы не знакомы со структурой данных RMQ, почитать о нем можно здесь.
Для начала, уменьшим все числа, не меняя их относительное значения, тогда все числа будут в переделе от 0 до n - 1. Нужно поддерживать два RMQ, каждое размером n. Пусть первое RMQ это Q1, а второе — Q2. Q1i будет содержать количество чисел i в текущему левом подмассиве, а Q2i — в правом. Для начала нужно добавить все n чисел в левое RMQ. После этого будем идти указателем r от n - 1 до 1, при этом поддерживая l — максимальный индекс такой, что пара (l;r) содержит не более чем k инверсий (в начале l равно n - 1). Количество инверсий, очевидно, нужно поддерживать, используя RMQ (используя операцию "сумма на отрезке").
В такой реализации время выполнения алгоритма равно O(NlogN).











Прошу прощения, а будет разбор на русском? К своему стыду, не всегда получается вникнуть во все детали английского текста.
К сожалению, на русском будет позже. Я постараюсь написать его как можно быстрее. Я подумал что английский будет более универсальным, поэтому написал его сначала.
I can't understand why doubled area is:|(x1 - x)(y2 - y) - (x2 - x)(y1 - y)|...can any one tell me why?
cross product?
Thank you...I am just on thinking about the meaning of this formula in classical geometry...a silly question...
In Div 1, Problem B, what is O(NsqrtN) solution?
For each two queries [l1, r1] and [l2, r2] we can easily change the first query to the second in no more than |l1 - l2| + |r1 - r2| operates.(adding or deleting the leftmost and rightmost elements and counting the number of times that each number appears)
Sort all the queries by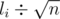 as primary sort key, and ri as secondary sort key. Now we can get a
as primary sort key, and ri as secondary sort key. Now we can get a 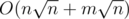 offline solution.
offline solution.
Why do you sort the queries by l/sqrt(n)
Split l into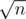 groups. We can ensure that
groups. We can ensure that 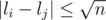 if i, j are belong to the same group.
if i, j are belong to the same group.
So we can calculate the complexity as follow:
a very underrated explanation thanks dude i was struggling with this problem
There is a much easier one. Just considering number x that occurs at least x times in sequence a. It's not hard to prove that there are at most 2*sqrt(N) numbers to be considered.
Can Anybody explain me , why are there at most 2*sqrt(N) of such numbers?. Thanks in advance.
(C[x] means the times that x occurs in sequence a) if C[x]>=sqrt(N), the number of this kind x is no more than sqrt(N). otherwise the number of elements in sequence a is greater than sqrt(N)*sqrt(N)=N if C[x]<sqrt(N), 1<=x<=C[x]<sqrt(N)
GREAT
220E — we use RSQ, not RMQ
220B: why has the proposed solution nlogn complexity? I mean, if for each x I need to sum up D_l, D_l+1 etc to answer to the queries (that in worst case start from 0 and end to x for each x), isn't it N^2?
you can use segment tree to query 0 to x....
BIT is easier and faster to implement here.
In explanation of 220C, what does this mean " (for the example above, it is texttt{2, 4}) " ? Does it mean that left set has a minimum distance of 2 and right set a minimum of 4?
\texttt was a tag, now it's fixed.
[2, 4] is the set of distances in right part, i. e. distance from 1 in sifted B to 1 in A (it is equal to 4) and distance from 2 in shifted B to 1 in A (it is 2).
Ну напишите же разбор на русском.
пишу
Прошу прощения, но не могли бы вы из задачи о сдвигах в примере из разбора описать все 7 состояний множеств S1 и S2?
Что с 33-им тестом Bdiv1? Ни у кого не заходит(
Говорите за себя :). У меня еще как заходит.
Не знаю, вроде все правильно делаю) Там он все время меняется почему-то) Из последних попыток почти у всех WA 33)
В разборе задачи 220E. Возможно подразумевалось не RMQ, а именно дерево отрезков? Прошу прощения, если я не прав.
RMQ — это задача, а дерево отрезков — это структура данных, или метод, если угодно.
В разборе написано "структурой данных RMQ". Примерно на это и хотелось обратить внимание. И дана ссылка на дерево отрезков. Если я не прав, то спорить не буду, в принципе суть решения и так понятна.
In problem A, for example, n = 3, if the init array is (3, 1, 2) (author's solution), isn't the sorted array is (3, 1, 2) -> (3, 2, 1) -> (2, 3, 1)? Did I mis-understand something?
PS: I know it's weird for a purple to stuck at Div2-A, but this one confused me a lot...
Edit: I got it, the sort happened after we enter function f[x-1], so it should be (3, 1, 2) -> (1, 3, 2) -> (1, 2, 3). I don't know what happened with my brain today...
220B — Little Elephant and Array, can anybody explain me how the update (add 1 to D[|p| — t], add -2 to D[|p| — t — 1], and add 1 to D[|p| — t — 2]) work?
I had a different approach
first of all count the numbers an remove numbers like x which occurred less than x times at all now you have at most O( sqrt(n) ) numbers.
for each of these store the indexes. for example store the indexes in which x occurred in vector[x].
now for each query(x,y) all you need to do is to binary search in each vector and find lower bound of x and upper bound of y( lets name them lbx and uby ) now we easily find out that x occurred ( uby-lbx ) times in [x...y]
it will solve the problem in O( N*sqrt(n) + Q*sqrt(n)* log( vector size ) )
can u give some advice , i write by mo's algorithm but it gives me tle http://codeforces.me/contest/220/submission/17425102
I think your algorithm runs in O(nsqrt(n)log(n) .It absolutely gets TLE. You can reduce log(n) to O(1) (remove or update operations) by just considering element which has value <= 1e5 . Cause every element greater than 1e5 can not contribute to the answer of a query . So you can use just a array instead of map
I have implemented the exact same logic but still getting a TLE.
Can you please take a look at my code?
72203897
Thanks in advance.
Your code complexity is m*k*log(sz) where k = total numbers whose occurrence needs be checked(maximum = sqrt(n)) and sz = size of total occurrence of that particular number in array(it can be sqrt(n) don't know the maximum bound). log(sz) which adds larger constant is responsible for TLE.
thank you for sharing your approach
In case if anyone finds the explanation for Div2D/Div1B confusing, just Google "MO's algorithm". Can't believe this magic man...
Little Elephant and Array can be solved with hashing. Since n*(n+1)/2<=100000, therefore n<=450, which is the condition for tightest constraints i.e. n=10000 and all numbers 'a[i]' are distinct and appear 'a[i]' times.
Solution: http://codeforces.me/contest/220/submission/20777330
how for for problem D complexity can be achieved O(mn)
Witua is known to set beautiful problems and this contest was fantastic !
Here are my solutions to the Div 2 problems of this contest.
In Div 2, problem D captured my imagination. So, I wrote an editorial about it here that explains both the approaches.
I love your editorial. its very comprehensive
could someone explain 220C. Little Elephant and Shifts bit more
How to solve Div 1 B using sqrt decomposition rather than MO's algorithm??
My solution for div1C is a little different. I know this is an old problem but I found it really interesting.
Let's graph the problem. Let's assume each cyclic shift happens in 1 second. Plot time along the x axis and the absolute difference in positions in both arrays for each value along the y axis.
Observe that there can be only two possible values of the slopes of the lines in the entire graph — +1 and -1. The line for a particular value will have slope equal to +1 if the position of the value in that instant's cyclically shifted array b is <= its fixed position in array, otherwise its slope will be -1.
Moreover it's easy to notice that for a particular value, its slope value changes a maximum of 2 times in its graph.
So we can maintain two range minimum segment trees with lazy propagation range updates for slope value = +1 and -1, each of which store the minimum y-intercept value at each integer instant from x = 0 to n-1. Then for at any given x, the answer is $$$ min \ ( i \ + \ minimum \ y-intercept \ of \ slope \ = \ +1 \ at \ x \ \ = \ i \ ,-i \ + \ minimum \ y-intercept \ of \ slope \ = \ -1 \ at \ x \ = \ i \ ) $$$
Total complexity is O(nlogn)
My submission: 57004696
(I've shifted the entire graph by 1 unit to the right to avoid using a segment tree with 0-indexing in my submission)
"Q1i will contain the number of numbers i in current left subarray. Q2i will contain the number of numbers i in the left subarray." ?
right!
For those of you getting TLE in Square root decomposition try using a different comparator or try changing the Maps to array
You can check my submissions 80679872
I dont get it to implement the tutorials solution to 220B - Little Elephant and Array
Can somebody link a submission implementing it? I did not found one because there are so much sqrt solution or something else.
Hopefully this one is clear enough...
And just look for MO's algorithm using square root decomposition i just learnt it yesterday actually..
The main idea in sorting the query and taking most possible advantage of overlapping queries since we can do it offline.
I also found this comment useful.
Kinda late, but here you go, hope this helps.
90807410
Please explain the 3 major update operations in your solution too it is not clear to me from tutorial and also from the submission.
learn a lot after solving Little Elephant and Inversions using binary indexed tree and cool idea of two pointers and inclusion exclusion principle
I solved it in a rather ridiculous manner. I created a segment tree to store the merge sort results at each recursion level. Then first I calculated the number of inversions at each index, from 0 to that index in one array, from that index to n — 1 in another array. Lastly, I used two pointers method to find the total number of inversions. If the total inversions in the array originally was greater than k, and the array had at least three elements, forward pointer pointed at 0, backward pointer pointed at 3, at each iteration, if the sum of inversions count of forward array (0 to forward pointer), backward array (backward pointer to n), and the number of inversions for each element in forward array to backward array (stored in variable named ptionk) was added to check if inversion count is greater than k, if so, backward pointer was incremented, else forward pointer was incremented. Each incrementation, I added the number of inversions increased or decreased (due to removing an element from backward array or adding an element to forward array) to ptionk. Am I the only one who did it like this
Any One Please Share Approach for 221A
simply take an n size array 0th element is n then store 1 to n-1 in the remaining place.