Hello,
Another contest from Samara reached Codeforces Gyms. It will be held on Saturday, November 5, at 10:00 MSK. Please don't participate if you know the problems.
And as usual,
The list of our previous contests
| # | User | Rating |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | tourist | 3993 |
| 2 | jiangly | 3743 |
| 3 | orzdevinwang | 3707 |
| 4 | Radewoosh | 3627 |
| 5 | jqdai0815 | 3620 |
| 6 | Benq | 3564 |
| 7 | Kevin114514 | 3443 |
| 8 | ksun48 | 3434 |
| 9 | Rewinding | 3397 |
| 10 | Um_nik | 3396 |
| # | User | Contrib. |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | cry | 167 |
| 2 | Um_nik | 163 |
| 3 | maomao90 | 162 |
| 3 | atcoder_official | 162 |
| 5 | adamant | 159 |
| 6 | -is-this-fft- | 158 |
| 7 | awoo | 155 |
| 8 | TheScrasse | 154 |
| 9 | Dominater069 | 153 |
| 10 | nor | 152 |
Hello,
Another contest from Samara reached Codeforces Gyms. It will be held on Saturday, November 5, at 10:00 MSK. Please don't participate if you know the problems.
And as usual,
| Name |
|---|



Do we have the solutions for these problems?
if not, can anyone tell me how to solve problem L :) Thanks.
Do 3 BFSes. Let G be the graph formed by the dependencies and G' be the same graph, with all its edge inverted. (changed direction)
Now, note that each correct labelling must "meet" at some point u (This may include 0, a or b), so the answer is the minimum possible value of this over all possible u :
Distance from 0 to u in G + Distance from a to u in G' + Distance from b to u in G'.
Is it guaranteed that the graph formed by dependencies is a connected one, or at least that A and B are in the same connection component?
If so, could you please tell me where it is mentioned/implied? Thanks)
you can find this description in the Input section.
Well, for instance, if we take a graph with no edges at all, wouldn't it suit this condition? We will be able to acquire all the skills, and we would only need 2 points to directly purchase A and B.
You might have misunderstood the problem but you looks smart because you tried to understand the statement carefully. Maybe, you've thought you can immediately get some skill which doesn't have any skills need to master in advance.
But here is a description which can correct your understanding.
If a skill has no skill it depend on, you can't satisfy the condition "at least one of talents..." and you can't get the skill. Such a case violates the constraints.
Understood it now, thanks a lot! :)
I thought exactly like you wrote before) Didn't consider this sentence restrictive while reading the problem description.
I tried doing a downward DFS from 0 storing at every node the minimum distance to A below it in the DFS tree, minimum distance to B and minimum distance to both A and B (means the no. of skill points needed to get both A and B if we have the current node.)
For a given node n, a_val[n] = min(a_val[child] + 1) for all children of n. b_val[n] = min(b_val[child] + 1) for all children of n. ab_val[n] = min(ab_val[child] + 1) for all children of n.
if(a_val[n] + b_val[n] < ab_val[n]) ab_val[n] = a_val[n] + b_val[n];
The answer is in ab_val[0]
The code is given below Solution Link
Could anyone please tell me why it's failing? (Test Case 18)
Thank you
im
up
What about D?
This is a max flow problem. A similar problem has appeared before ( Kyoto University Programming Contest 2016 — Problem E ), the difference is that the squares are weighted, we only need to block one square and we have to provide a certificate.
I've explained the solution in the link above. The only modification needed is the capacities of each square (change it to the respective weights). To construct a possible solution, we just have to find the minimum cut.
My code : here (I've used min cost flow as initially I thought that min cost flow is needed, but it turns out that max flow is sufficient)
Can you please tell me the solution of B and C?; I got WA in B, and RTE in C;
Problem C: Call the output array res[]. For all number a from 0 to p-1, we calculate b = a^2 % p. Then res[b] = a.
B: Sort all dragons by (a — b), then do simulation from the end: imagine you have zero warriors at the beginning, then you fight dragons in sorted order, and after each fight you resurrect some warriors. If you don't have enough warriors, add some to be able to fight next dragon (you need (a — b) warriors to fight dragon because we're resurrecting warriors, not killing them).
There's some reasonable explanation why it works: if we sort dragons by amount of warrioirs needed to fight them, then total amount of warriors after all battles with dragons in sorted order will be minimal, it's greedy algorithm. Try represeniting dragons as oriented segments from a to a — b in number line to see why it works.
Well, I actually had more reasonable explanation when I was solving this problem, but that was 1.5 months ago and I already forgot it :D
My solution: http://pastebin.com/snwTke9g
Can anyone share the proper solution to question K?
During the contest, I observed that the answer is independent of rotation, and scaling the initial distance by a factor of D increases the safe area by D^2. Since the case for distance 1 is given in the test case, I just multiplied the squared distance between the dragon and the palace by 0.916297857297023. It works, but is highly unsatisfying.
It seems like 0.916297857297023 came from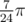 but idk why this is the answer either.
but idk why this is the answer either.
What you described was an intended solution.
Jury got the answer using this article: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radiodrome and some binary search and numerical integration. It calculates 7 correct digits in 1 second.
There is also a math solution, here is a document (in Russian, but you should be able to read formulas): https://yadi.sk/i/-BcFxkTry7mZm
That's actually slightly "bad" question setting (in a twisted sense), since technically the sample solution could only be correct to 10e-6 absolute error (hence not 10e-6 relative error) and larger solutions would WA (We would need to guess slightly more and slight less than the sample solution for 100% confidence of AC).
Thankfully, it seems the sample solution is correct.
Thanks for the links as well :)
what is the solution procedure of problem G?
Scanline. Events are: zork and axe. Sort all events by weight (for zorks weight is minimum axe weight they need), then go by events in reversed sorted order (from biggest weight to smallest). Maintain a set where you store curvature of all avaible axes. When you meet axe, add it to the set. When you meet zork, give him axe of minimum avaible curvature he can take (in other words axes.lower_bound(zork.curvature). Try imagining all events as points (x: weight, y: curvature) on coordinate plane to see why it works.
My solution: http://pastebin.com/j7JtgWZu
I came up with the same solution but It's RTE on test 24
can you find what the bug on my code
Thanks for your contribution man~ !
Problem K. I think it's rare problem where if you do not know solution, you can use the answer of 1st test to generate other answers. And Jury can't hide answer to test 1, because they must show a least one. E.g. 22061070
Solution "multiply answer from sample by square of distance between two points" was intended by jury. Read dalex comment above.
Can you give me a hint for problem A ?
Answer is maximum element in array. It can be proven by induction.
what is the test number 6 for H? I got 6 times wa for this.
(?))?(?)Solution for I and J please. Thanks
I: find vertex of minimum degree and place policemen in all verticles except vertex of minimum degree and its neighbours.
J: every time a[i] > a[i-1] it means that there're a[i] — a[i-1] photos beginning at building i. So you have to find sum of max(a[i] — a[i-1], 0) for all i = 1..n (a[0] = 0)
How to solve M?
Simulate a direct elimination table with the n people. Every time you get i < j, store i in the vector of all people that lost against j. When you only have one guy left, then you now it is the guy with the highest rank. This needs n-1 queries.
Then, simulate another elimination table with people that lost against the guy with the highest rank. This needs O(log(n)) queries. Therefore, you will always need strictly less than n+24 queries.
Note that, if you search for the guy with the highest rank naively, than the second part may need O(n) queries in the worst case, which is not good.
Can anybody tell me how to solve problem H or give me some tests? I still got wa on test 6.
Let tab[i] the number of '('s that are necessary in the first i characters in order to get a valid sequence, then compute t[n], tab[n-1], ... tab[1] (this is actually dynamic programming).
Then, using this array, replace '?'s greedily from left to right in the sequence.
Then, check whether the resulted sequence is valid or not.
Can anybody give me some tests on H's test 39? I get WA on it...
The algorithm is quite like that of noelnadal's. But I do not know what is going on...
Generated by this code:
Can anyone tell me why problem B we have to sort a-b descending order ?
How to approach F?
Pretty sure that it's not really hard to come up with a counter example for my idea, but sadly i can't think about anything else.
My approach is for each tuple {x, y, z} i maintain all values of x in a vector same for y and z.
Then i sort them maintaining the index with them.
Then for each tuple i should check if i should consider it or not, how?
if it's larger than the x[0] then i am sure that this X-i is valid now i should only check for the other 2 pairs.
When i check for them i check for the index of x[0].
Anyway here's my code hopefully it's clean enough..
As all parameters are distinct, the answer is always 0 or 1. If it was 2, we could make these two losers face each other and someone would win.
Find one potential candidate with the for cycle, similar to the finding linear minimum in the array. The comparator is strange (not transitive, ...), so do another check to find if he really loses to everyone else.
Sorry for necroposting, but could I have a solution for problem L, really thanks!
You're not excused, read the first comment and reply