703A — Мишка и игра
Всё, что Вам требовалось сделать в этой задаче, — посчитать количество раундов, в которых победит Мишка, количество раундов, в которых победит Крис. Для этого следовало завести две переменные countM и countC. Если в очередном раунде Мишка выкидывала на костях большее значение, чем Крис, то 1 следовало прибавлять к переменной countM. Если меньшее — к переменной countC. В конце нужно было сравнить полученные значения и вывести ответ.
703B — Мишка и путешествие
Рассмотрим первую столицу. Заметим, что стоимость исходящих из неё дорог равна c[id1] · (sum - c[id1]), где sum — суммарная красота всех городов. Таким образом, переходя от одной столицы к другой, мы сможем посчитать суммарную стоимость дорог, исходящих из столиц. Однако не стоит забывать, что дороги между столицами в таком случае будут посчитаны дважды. Для этого на очередном шаге мы должны вычитать из переменной sum значение красоты текущей столицы. В конце нам остаётся посчитать стоимости дорог, проложенных между "не столичными" соседними городами.
Асимптотика полученного решения — O(n).
703C — Крис и дорога
Для начала представим, что автобус в действительности стоит, а сами мы передвигаемся "вправо" с постоянной скоростью v. Тогда заметим следующий факт: нам всегда выгодно перемещаться по прямой вида y = (u / v) · (x - v · t0), где t0 — время, спустя которое мы начинаем своё перемещение по пешеходному переходу. Ответ же будет определяться как t = t0 + (w / u). Теперь рассмотрим два варианта развития событий.
Если t0 = 0, то мы начинаем наше движение сразу же. В таком случае нам следует проверить, что прямая не пересекает многоугольник (т.е. либо мы можем перейти дорогу перед автобусом, либо автобус уже прошёл и не угрожает нам).
Если же проверка не удалась, то нам следует найти такое минимальное положительное значение t0, при котором описанная прямая будет касаться многоугольника. Это может быть сделано при помощи бинпоиска.
Асимптотика решения — O(n log n).
Упражнение: Улучшите асимптотику до O(n).
703D — Мишка и интересная сумма
Посмотрим, что из себя представляет запрос. Несложно заметить, что ответом на него будет являться XOR-сумма всех элементов на подотрезке с XOR-суммой различных элементов на том же подотрезке. Первое мы умеем находить за O(1) с предподсчётом за O(n) (используя префиксные суммы). Что же касается второго, то научимся для начала решать похожую, но более простую задачу.
Пусть нам поступают запросы вида "найдите количество различных чисел на подотрезке". Отсортируем все запросы по правой границе и будем последовательно итерироваться по элементам массива, попутно заведя массив last, где last[value] — последняя позиция вхождения значения value в массив на обработанном префиксе. Допустим, мы обработали все элементы до позиции r включительно. Тогда заметим, что ответом на запрос на отрезке [l, r] (l ≤ r) будет являться 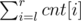 , где cnt[i] = 1, если last[ai] = i, или 0 в противном случае. Поддерживать эти значения в массиве cnt довольно просто, для этого при переходе к очередному элементу ai нам всего лишь требуется сделать следующие присвоения: cnt[last[ai]] = 0, cnt[i] = 1, last[ai] = i. Если же для поддержания значений cnt использовать дерево отрезков или дерево Фенвика, описанную сумму мы сможем находить за O(log n).
, где cnt[i] = 1, если last[ai] = i, или 0 в противном случае. Поддерживать эти значения в массиве cnt довольно просто, для этого при переходе к очередному элементу ai нам всего лишь требуется сделать следующие присвоения: cnt[last[ai]] = 0, cnt[i] = 1, last[ai] = i. Если же для поддержания значений cnt использовать дерево отрезков или дерево Фенвика, описанную сумму мы сможем находить за O(log n).
Теперь вернёмся к нашей задаче. Всё, что нам требуется сделать, — заменить присвоения cnt[i] = 1 на cnt[i] = ai и считать не сумму, а XOR-сумму. Таким образом, мы научились решать задачу с асимптотикой O(n log n).
P.S.: Существует также решение этой задачи за O(n sqrt n) с использованием алгоритма Мо, однако мы постарались отсечь его. Кажется, получилось :D
703E — Мишка и делители
Для решения этой задачи воспользуемся динамическим программированием.
Пусть в dp[i][d] будет храниться минимальное количество таких элементов на префиксе размера i, что их произведение кратно d. Переход в этом случае будет следующим: dp[i][d] = min(dp[i - 1][d], dp[i - 1][d / gcd(d, ai)] + 1). Формально это можно объяснить тем, что нам всегда выгодно как можно больше "брать" от ai. Ответ будет храниться в dp[n][k].
Давайте оптимизируем наше решение. Заметим, что в качестве значений d нам следует использовать исключительно делители k (которых, кстати, в худшем случае будет 6720). Что касается gcd, то его мы можем находить за O(primes(k)), где primes(k) — количество простых чисел в разложении k. Сами же делители следует перенумеровать в соответствии с их разложением на простые множители.
Таким образом, для получения AC нужно было оптимизировать описанную выше динамику, добавив к ней минимизацию суммы используемых элементов. Итоговая асимптотика — O(n · divs(k) · primes(k)).











Задача Д
Что такое Мо?
Вот здесь хорошо написано про него.
My take on 703C - Chris and Road:
For each vertex of the polygon, consider its y coordinate and the point in time where it crosses the path of the pedestrian (which may be negative). There are two possibilites:
a) We can cross before the bus reaches us. Whether this is possible can be easily checked by checking if for each vertex of the polygon, that the pedestrian can be at 0,y earlier than when the point of the polygon crosses the path. In this case the answer is simply w / u.
b) In the other case, we have to go behind the bus. In this case, for each vertex, calculate ti = (w - yi) / u + xi / v. This is the time the pedestrian would need to reach the other side if the she started from each vertex of the bus right when it crosses the path. Because the polygon is convex, we know that this is the optimal valid path behind the bus iff we pick i such that ti is maximal. The only exception is when we actually cannot reach the required yi at least as fast as the bus. So the answer is max(t1, t2, ..., tn, w / u).
All of this can be computed in O(n).
Hi, can you please explain how the optimal path would be the one for which t is maximum in case (b)
http://codeforces.me/contest/703/submission/19666971
Just sort the points by increasing y, and check for the events which happens later: The point (x,y) passing through point (0,y) or the time required for Chris to reach (0,y) from the previous y position.
Consider all possible paths behind the bus. We can always improve the time we need to reach the other side by starting earlier, i.e. moving out path to the left in the projected interpretation of the problem. If we start with a path which does not touch the bus at all, we can keep starting earlier until we touch the bus somewhere (or until we don't wait at all and still reach the other side behind the bus). We don't want to start earlier once we exactly touch some vertex i, since that would mean that we hit the bus at yi. The time we coincide with i is xi / v. From there, we need (w - yi) / u more seconds to finish crossing the street. The sum of these two times is ti. Since we continually improve our time by starting earlier as described above and we picked the first possible ti, we have picked the maximum ti. Picking any tj other than the maximum ti would describe a path that hits the bus at yi.
Great solution! I love it. I have a question. Since we are picking the leftmost path which doesn't collide with the bus, does it make sense to just look for the point which has the highest x-coordinate and calculate the t = (w-y)/u + x/v for this coordinate alone?
Since this should be the maximum t anyway, it will produce the same answer as yours. If I am mistaken, could you provide me with a counter example? Thanks!
Here is a counterexample:
The vertex with maximum t is
1 0.When will practice be opened? It still shows system test is pending and I can't submit my code. :(
can't understand problem D. Please provide source code on it.
My solution
I used Fenwick tree (ll bit[N]) and did a coordinate compression (int b[N] — since values are very big, but we have at most 1^6 different values).
The ideia is that to calculate XOR of elements that appear even times is the same as the XOR between the XOR of elements that appear odd times (and that's the same as the XOR of the whole subsegment, because if some element appear twice it will cancel in XOR) and the XOR of unique elements in the subsegment. It can be a little hard to understand, but write on paper and go testing small numbers to see that this is true.
The XOR of the whole segment can be easily calculated using partial sum (in this case partial XOR: pre[i] = pre[i-1]^a[i]).
The XOR of unique elements can be found using a range query/point update data structure (Fenwick tree or Segment Tree) and iterating in each element of the array. Since you want only unique elements, you store the rightmost/last appearance of some element (because you will query from the element you are to the left, so storing the rightmost appearance assures the element you be contained in every segment that begins before the last appearance). To do this you iterate from i = 1 to n, if element already inserted (last[element[i]] != 0) you remove the element from this position (using the point update of the data structure). After that you update the last position of this element and add the element in this new position. For every query that right end is equal to i you query in your data structure for the query range (XOR of unique elements in range) and XOR with the whole segment (pre[r]^pre[l-1] — XOR of elements that appear odd times), and that's the answer of the given query.
Hope this helps. Any doubts be free to reply.
hello my solution got wrong answer on test 14. My idea is similar to above. i used segment tree. Please check it and i don't know where i made mistake. http://codeforces.me/contest/703/submission/19666191
I've being testing many things in your code. Found a small issue but was not the main problem... After 1h or more I decided to change your defines...
The first problem is the long long instead of int. Since the numbers can be bigger as 10^9, the XOR can be bigger than int limit. You can use unsigned int, but long long is the safer way.
The other issue (the hard to find one) is with defines... Try to use const instead of defines for constant numbers. You used #define _N (int)1e6+5, and declaring the variables you did tree[_N * 10]. Resolving the define will result in tree[(int)1e6 + 5*10]. You see the issue, right? Defines are bad in many ways, so use defines only if you can't use other things (use typedef to create new types, as typedef long long ll; to shorten long long, and const to constant values, as const int _N = 1e6+5;).
Your solution with modifications
Yes. Thank you very much. I'm very glad to understand my mistake.
Can you please explain how the xor can exceed the int limit? According to my calculations ceil(lg(1o^9) = 30. So the maximum xor will have at most 30 bits set which is 2^30-1 and is less than 2^31-1 (int limit).
You're right, xor won't exceed int limit. I saw this after posting and decided not to edit. Anyway using long long won't do bad, but is not necessary in this case, thanks for replying!
In case if anyone still gets TLE in this task, using un-tied cin & cout is not good enough this time. Better rewrite your code with scanf printf.
Good Job kogyblack! Good Explanation :)
In problem E, why can't we use the euclidean algorithm to find the gcd between
danda[i]?How do I know when to use Mo's algorithm for such questions? I have done similar problems with similar constraints or even higher constraints using Mo's Algorithm. In contest I tried optimizing Mo's algorithm several times and as a result got 5 TLEs on case 14 :(
So please tell me if is there is a way I can identify if O(n*sqrt(n)) will work for a problem with primary constraint N lying around 10^6. If not,then for what values of N should I go for Mo's algo.
O(N * sqrt(N)) doesn't work here.
Intended solution is O(N * log(N))
here N = 106
so O(N * sqrt(N)) would be of order 109, which is hard to pass even though you make good I/O optimisation.
Use MO's Algorithm for N = 105 order.
I wouldn't say that 109 is "hard to pass". 10^9 simple operations' time is close to one second (See this: 19666793)
Mo is known to have VERY small constant factor, so it might pass in 3.5 seconds.
However this guy didn't manage to pass, even though his constant factor seems to be really small.
Even this guy didn't manage to pass :)
But this guy managed to pass :)
But passing in 3.5s with Mo isn't only possible in CF? I mean CF judge looks so fast than any other judges.
Yay! I have the same solution for C. Here is some explanations from me with easy checking whether line intersect with rectangle:
Fact: if pedestrian must to slow down his speed or even to stay without moving (in other words, he can not run directly to other boarder from the begining at full speed), than staying in starting point from the begining of the time for a while would be optimal. Note, that if in start time pedestrian can not walk to the next border of road and not to be hit by the bus, then for some time while the bus will ride to left he won't be able to do this so. Thus, we need to check this. About check I will told you later. If true (he can run directly to other boarder from the begining at full speed) than answer is w/v. Otherwise, we need to find how many pedestrian need to wait in start point. We can do binary search to find this (because of note that I written above) using the same check I had noticed before. Note, that relatively bus vector of pedestrian's speed has coordinates (v, u). Finally, check. It's parameter — time of delay before starting working. To check we need to find whether line through speed vector intersect a rectangle. We can find signs of oriented triangle area between vector of speed and vector (Xi-t*v, Yi). If there two different signs, than line through vector of speed intersect the rectangle after time t. Check my code, there are implementations of all I have said above and it is quite simple.
In problem C, how to determine that a line intersects the polygon?
Line intersects polygon if it intersects any of it's edges.
Simply iterate through all edges and check if they intersect with line or not.
You just need to check the set of signs of values calculated for each polygon point by the line equation Ax + By + C. If there are not both 1 and - 1 simultaneously, all points lie from the only side of the line, and it does not cross the polygon.
Can someone please elaborate the solution to E? I don't understand the dp relation. Thanks!
The point is to find the minimum step of reaching d by taking the prefix array of i. You either take the previous prefix value, or track it from the previous point, where taking a[i] will transfer to the state lcm(d,a[i]) (while only considering the prime components of k since other doesn't matter)
I am quite lost in the implementation of the optimization though, so I can't help you out in that part. :/
Has anyone solved Div2D with persistent segment tree . My Submission is giving Runtime Error on TestCase 14.I don't have any clue of the reason and have allocated more than enough memory (I think). The idea of pst's root[i] is to store xor of distinct numbers which are as close to it as possible.
Has anyone solved Div2D with persistent segment tree . My submission is giving Runtime Error on TestCase 14.I don't have any clue of the reason and have allocated more than enough memory (I think). The idea of pst's
root[i]is to store xor of distinct numbers which are as close to it as possible.I'm not sure. Our solution with persistent segment tree works even slower, than our solution with Mo's algo.
Can you share your persistent segment tree solution. My solution answers queries in
O(logn)online.I think you didn't apply for enough space...You applied 2111111 * 8 == 1700000 Nodes , but you need at least 1000000 * log( 1000000 ) = 20000000 Nodes...
В С указана асимптотика O(n log n), хотя верная O(n log 10^9)
Интересно, что O(n log 10^9) = O(n).
n log MAXCOORD
I am confused...the man's speed can be always changing, for example ,v=2t^2,then may be less time?? i mean ,how to prove y = (u / v) · (x - t0) can create the minimum answer?
Hi everyone.. I am trying to understand the solution of problem D . I am not able to figure out what does moving to next position in line "When moving to the next position we have to make the following assignments: " mean. Also while taking the sum if last position of ai is not I shouldn't we subtract 1 from the sum as 1 has been added before for a repeating element. That is with my assumption that count array shows number of times ith element is present.. Thanks.
IN 703C,the equation you wrote, dimensions does not match, one is time, another is distance.. The correct equation is y = (u/v)(x-v*t)
Sorry, fixed.
What is the variable 'd' in problem 703E — Мишка и делители tutorial?
Can someone please explain.
Fixed. There should be "Suppose dp[i][d] is the minimal number of elements on prefix of size i, that their product is divisible by d".
Anyone solved D using segment tree because I have no idea about Fenwick tree?
Don't know if you are still alive :P but here you go 92688725
This is My Submission for problem D can you tell why this submission is showing TLE. I have used segment tree.
Sorry I got the mistake ;).
Earlier I was passing a and b as value.
I am not able to pass problem E with the same complexity mentioned in the editorial. I think the time limit is too tight. Please check the solution.
I tried similar solution as yours and got TLE too. the function gcd is log(k), whick is bigger than prime(k), and that's why the tutorial use some other method to calculate gcd.
Откуда взялась оценка количества делителей 6720 в задаче 703E - Мишка и делители?
Число с таким количеством делителей — 963761198400. Числа с большим количеством делителей, которое не превышало бы 1012, нет.
Чтобы вывести подобные числа, достаточно написать перебор, который строит минимальные числа по наборам степеней простых (как известно, количество делителей напрямую зависит от такого набора степеней), беря только минимальные простые и раздавая большие степени меньшим простым.
Это кстати можно сдать 100467A - Игра с числами, запустить для N=10^12 и убедиться в достоверности :)
Как перенумеровать делители в соответствии с их разложением на простые множители в задаче 703E - Мишка и делители?
Since k can be 10^12 ,how to get the prime factors of k ?
Time limit on E is very tight. I had to hard code cases.
703D: "Посмотрим, что из себя представляет запрос. Несложно заметить, что ответом на него будет являться XOR-сумма всех элементов на подотрезке с XOR-суммой различных элементов на том же подотрезке."
Ничего себе несложно! Это совершенно неочевидно. Как доказать этот факт?
Понял сам.
Problem E: "We also need to renumber our divisors according to their prime decomposition."
What does it exactly mean? Why do we even have to decompose the divisors?
-
Hi...Can annyone tell me why my solution of Div2D uding Mo's isn't passing on test case 14? it is getting TLE..Even after increase the block size it is still getting TLE.. my solution of Mo's Algo: http://codeforces.me/contest/703/submission/29365587
For problem Div2D, i have used MO's algorithm.But my code got TLE in case number 15!Is there any way to solve this problem using MO ?Please,help me then! 32085407
You need:
fastest IO (fread / fwrite)
compress coordinates
rearrange the coordinates in the original order of given array from left to right
use optimized Mo's compare function
sgtlaugh solution
my solution
I think problem E it is not very difficult, but it has a very adjusted TL, IMO autors should have proposed a more comfortable TL.
My submission 34821624
Perhaps the problem E's time limit is too harsh. Now Codeforces has removed C++11,and the fastest solution of C++14 is 600+ms,but the limit is only 1s.
So could you plz expand it to 2s or more?
thx