Задача A. Div2.
Заметим, что число x может встречаться в столбце i только один раз — в строке x / i. Переберем столбец i, проверим, что x делится нацело на i, а также x / i ≤ n. Если все условия выполнены, обновим ответ.
Асимптотика — O(n)
Задача B. Div2.
Рассмотрим два случая: n > m и n ≤ m.
Пусть n > m, рассмотрим суммы на префиксах. По принципу Дирихле, найдутся две равные суммы по модулю m. Пусть Slmodm = Srmodm. Тогда сумма чисел на отрезке с l + 1 по r по модулю m равна нулю, то есть ответ точно "YES".
Пусть n ≤ m, то решим задачу динамикой за O(m2). Пусть can[i][r] — можем ли мы, используя первые i предметов, получить остаток r от деления на m. Переходы в динамике понятны: либо мы берем предмет и переходим в состояние can[i + 1][(r + ai) mod m], либо не берем и переходим в состояние can[i + 1][r].
Асимптотика — O(m2).
Задача A. Div1.
Пусть Петя не спросил число pk, где p — простое, а k ≥ 1. Тогда, Петя не сможет отличить число pk - 1 от числа pk.
Значит, нужно спросить все числа вида pk, где p — простое, а k ≥ 1. Несложно убедиться, что это позволит угадать и все остальные числа.
Асимптотика O(N1.5) или O(NloglogN) в зависимости от теста на простоту.
Задачи B. Div1.
Рассмотрим дерево-ответ. Заметим, что центры этого дерева могут перейти только в центры при применении перестановки. Это означает, что в перестановке обязательно должен быть цикл длины 1 или 2.
Пусть в перестановке есть неподвижная точка. Тогда мы можем подсоединить ребрами к этой вершине все остальные. Несложно убедиться, что это корректный ответ.
Например, пусть дана перестановка (4, 2, 1, 3). В перестановке есть неподвижная точка 2, поэтому подсоединим ко второй вершине все остальные. Получатся ребра дерева (1, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4).
Пусть в дереве-ответе есть два центра. Удалим ребро между ними, дерево разобьется на две компоненты. Несложно понять, что они должны перейти друг в друга при применении перестановки. Это означает, что все циклы перестановки должны быть четной длины.
Понятно, как построить ответ, если все циклы четной длины, и есть цикл длины два. Проведем ребро между вершинами из цикла длины два, вершины всех остальных циклов будем присоединять по очереди к центрам.
Например, рассмотрим перестановку (6, 5, 4, 3, 1, 2). В перестановке есть два цикла: (3, 4) и (1, 6, 2, 5). Соединим ребром вершины (3, 4), все вершины другого цикла присоединим по очереди к этим двум вершинам, получим ребра (1, 3), (6, 4), (2, 3), (5, 4).
Асимптотика — O(N).
Задача C. Div1.
Разобьем квадрат 106 × 106 вертикальными линиями на 1000 прямоугольников 103 × 106. Пронумеруем эти прямоугольники от 1 до n в порядке слева направо. Обойдем их тоже слева направо, а внутри каждого прямоугольника обойдем точки по возрастанию y-координаты, если это четный по номеру прямоугольник, и по убыванию, если нечетный.
Посчитаем длину такого пути, будем считать независимо по каждой координате. По y-координате мы пройдем суммарно 1000 прямоугольников от 0 до 106, то есть суммарно 109, По x-координате, чтобы дойти до следующей точки внутри прямоугольника, мы потратим не более 1000 на точку, и 1000 раз пройдем не более 2000 до следующего прямоугольника, то есть суммарно 109 + 2000000.
Итого, длина пути не более 2 * 109 + 2000000, что подходит под ограничения на длину.
Асимптотика — O(n * log(n))
Задача D. Div1.
Будем оптимизировать первое же решение, которое приходит в голову за O(m * dmax): посчитаем can[t][v] — можно ли добраться до вершины v, пройдя по ровно t ребрам.
Теперь заметим, что множество ребер, по которому мы можем ходить меняется только m раз. Отсортируем ребра в порядке возрастания di, т.е. для всех i di ≤ di + 1. Будем считать динамику can[t][v] только для t = di. Пусть мы хотим перейти от can[di] к can[di + 1]. Поскольку набор ребер не меняется с момента di до di + 1, мы можем возвести матрицу смежности в степень di + 1 - di и применить ее к can[di].
Пусть мы насчитали все can[di][v]. Теперь зафиксирует ребро с максимальным di, по которому мы пройдем в нашем кратчайшем пути. Мы знаем все вершины, в которых мы можем находиться в момент di, далее нужно найти кратчайший путь из них в вершину m по открытым для нас ребрам и обновить ответ. Матрицу кратчайших расстояний можно посчитать Флойдом, поэтому обновление ответа не составит труда.
Получилось решение за O(m * n3 * log(dmax)), которое, к сожалению, работает долго.
Далее нужно заметить, что матрица смежности состоит из ноликов и единичек, поэтому её можно возводить в степень битовым сжатием за O(n3 / 32). Это дает решение за O(m * n3 * log(dmax) / 32), что спокойно заходит по времени.
Задача E. Div1.
Сначала решим чуть более простую задачу: пусть вне зависимости от двудольности/недвудольности запросы выполняются, а от нас требуется лишь ответить, будет ли граф двудольным/недвудольным после запроса.
Тогда мы могли бы применить решение, похожее на решение задачи Dynamic Connectivity Offline за O(nlog2n). Опишем его подробнее:
Вначале пусть ребра только добавляются. Тогда можно воспользоваться системой непересекающихся множеств, где, кроме предка, будем хранить четность пути до предка, а также флаг двудольности текущего графа. Теперь мы можем найти четность пути до корня — просто пропрыгать до предка, проксорить четности. Теперь, когда мы проводим ребро между двумя компонентами, мы можем посчитать четность путей до вершин этой ребра, а значит, и установить четность прыжка из корня одной компоненты в корень другой компоненты. Если ребро проходит внутри одной компоненты и четности пути до корня совпадают, нужно убрать флаг двудольности текущего графа.
Теперь пусть ребра иногда удаляются. Для каждого ребра и каждого цвета мы знаем отрезки запросов, когда это ребро будет в графе заданного цвета. Давайте построим дерево отрезков на запросах, в каждой вершине будем хранить список ребер, которые будут включены на этом подотрезке. Каждый отрезок дерево отрезков разобьет на log кусочков, поэтому в сумме количество добавлений ребер на кусочке будет порядка n * log.
Теперь, можно обойти это дерево отрезков в глубину с системой непересекающихся множеств с откатами. Мы входим в вершины, применяем все запросы добавления ребра в данной вершине, обходим потомков, а затем откатываем снм до состояния, в котором оно было на входе в эту вершину. Когда мы находимся в листе, отвечаем на соответствующий запрос.
Вернемся к нашей задаче. Вышеописанную технику в явном виде мы применить не можем, потому что не знаем точно, на каких отрезках запросов ребра будут существовать.
Зато мы можем сделать следующее. Изначально применим операцию до первого момента появления ребра в запросах. Теперь, когда мы находимся в листе, мы узнали, какого цвета это ребро будет до следующего его появления в запросах. Поэтому, давайте сделаем обновление на отрезке со следующего запроса до следующего появления этого ребра. Для каждого листа мы сделаем не более одного обновления, поэтому суммарное время работы O(nlog2n).
Асимптотика — O(nlog2n).
Если что-то неясно, непонятно или невнятно написано, задавайте любые вопросы.










thanks for fast Editorial ;))
Динамика в див 2 Б, серьезно?
Скажем так могли бы сделать, чтоб динамика(рюкзак) за O(n * m) заходила.
Могли бы сделать, чтоб динамики не было вообще, потому что ни один новичок никогда в жизни не придумает и не напишет какую бы то ни было динамику.
С этим согласен, рюкзак придумать самому нереально. Но это бред, если ты придумал задачу и идея точно такая же, но решение за 10^9 не проходит , хотя порой срабатывает. То есть это не Div2 B
Ну, вот это решения с
bitsetом :) 12937772На самом деле здесь необязательно применять динамику. Можно аккуратно организовать перебор.
Будем пытаться получить все возможные новые суммы подпоследовательностей для каждого элемента последовательности. Решение в лоб за O(m * n) не подойдет по времени. Попробуем оптимизировать.
Трюк в том, чтобы не просматривать одни и те же варианты несколько раз. Для этого будем вести историю уже встреченных сумм. При добавлении новой суммы инкрементируем счетчик времени t. Для каждого просматриваемого значения a[i] запомним значение счетчика времени до его обработки T[a[i]] = t. Пусть текущее значение с = a[i] % m было до этого последний раз было встречено в момент времени t1. Нет необходимости просматривать все встреченные до текущего момента суммы. Вместо этого можно ограничиться только вновь добавленными: T[t1]..T[t]. Таким образом для каждого возможного значения 0 <= (a[i] % m) < m будет просмотрено не более m сумм подпоследовательностей.
Итоговая сложность O(m^2)
В отличие от решения, описанного в разборе, нет необходимости отдельного рассмотрения случая n > m и можно обойтись без динамики.
PS: ссылка на решение http://codeforces.me/contest/577/submission/12944258
Можно было без динамики: 12935754
Вы будете смеяться,но она заходит http://codeforces.me/contest/577/submission/12934365
Тесты просто на высоте
Спасибо. Парень всё по делу сказал. Чё вы минусуете, нужно malcolm минусовать за такую задачу и тесты.
У graciocode честное решение за O(m2).
Нечестное за O(n * m) 12963746. Задача сама мне понравилась, если честно.Бомбит меня с того, что тесты слабые.
То, что ты прислал — это O(n + m2), поскольку среди первых m элементов найдется ответ, участник выведет "YES" и выйдет из цикла.
Не очень понятно, почему среди m элементов найдётся ответ. Типа они дадут m остатков, а уже остальные дадут один из m, так?
O(nm) легко заходит, если избавиться от взятия модуля в цикле. Т.е. писать
вместо
12952911
Просто заходит под MS C++, даже если модули часто брать. Хватит терпеть то, что 10^9 под MS C++ заходит, а под GNU C++ нет.
Вообще-то задача А div 2 решается за О (N ^ 0.5)
В зависимости от реализации.
Решение за O(n ^ 0.5) — очевидная и неуместная оптимизация.
Почему неуместна?
Потому что N маленькое. А в задаче, которую надо решать очень быстро, думать о оптимизации верного решения как-то странно.
Мне и в голову не могла придти такая дикая мысль, как перебирать делители числа N за линию, а не корень. Надо всегда писать код нормальный, а не делающий кучу ненужной работы.
Надо всегда писать решения быстро и правильно, а не оптимизировать. Это же спортивное соревнование, а не промышленное программирование. Как только вы перебираете делители за корень, возникают случаи, которые нужно правильно рассматривать и не забыть про них. В реализации за O(n) случаев нет. И именно об этом надо думать, когда вы начинаете писать решение.
Здесь на этом сложно попасться, да и спор особо ни о чём, но в других задачах такой подход может привести к неудачам.
Неважно, я попутал div2A и div1A :(
Не знаю, при чем в этой задаче тест на простоту. За корень я перебираю делители
Ой :( Я принял div2A за div1A и писал, соответственно, о ней.
В задаче А нет никакого теста на простоту, в моем решении есть только один цикл, и работает он за корень
in problem B Div2, Modulo sum,
for n > m, can someone elaborate on how pigeonhole principle implies there exists 2 sums with same value in prefix sums.
Also can't we use the DP for n > m as well?
UPD: Understood and got AC. Here's my AC solution according to editorial above.12948929
We can't use DP if n > m since it will be performance for O(n^2) which really slow.
We have a1, a2, ... an. Make array Si = sum ak from 1 to i (S1 = a1; S2 = a1 + a2; ... ).
If n > m, there are Si and Sj which Si % m = Sj % m and j > i. So (Sj — Si) % m = 0. Since Sj — Si = a1+a2+...+Aj — (a1+a2+...+ai) = a(i+1) + ... + aj. So we've got answer.
it will be O(n*m) not O(n^2), but still slow
but if you teminate as soon as you find there is a solution, the complexity would be O(m^2) due to the conclusion mentioned above.
I solved this by Dynamic programming:
First sort all the values in non-decreasing order then apply dynamic programming on first 10^4 values only, and this is should work :D
And why only first 10^4 ?
Ok, there is no proof for this, but when you're inside a contest and you will not lose any thing if you send a wrong answer, then try different ways to solve.
10^4 * 10^3 for the state of dynamic programming, so I reduced the time from (10^6 * 10^3 to 10^4 * 10^3) but I sorted the values! and it worked.
Can we not use the prefix sum solution for "n <= m"?
No because the pigeonhole principle can't be applied there and hence there is no guarantee that there exists two sums Si, Sj such that Si % m = Sj % m
Could you show me a case when n == m the answer is 'no'? I understood for n > m, but why not n >= m?
Actually it can be applied here. SUM%m only has m states and 0 is a valid state so we only have m-1 invalid states. Thus since each added number can reach at least one new state its impossible to find m numbers which can't generate a multiple of m.
Also the only cases where m-1 numbers can't generate a multiple of m is when we have m-1 copies of a number num relatively prime to m. We can see that this is true since each new number will generate at least two new states if it is different from all of the past numbers and if num is not relatively prime to m then it will reach a multiple of m in less than m steps.
I get it now. Thanks for the explanation!
Thanks for the reply balalaika
I am still unable to prove using pigeonhole principle that there will definitely exist two sums Si, Sj such that Si % m = Sj % m.
It would be very kind of you if you could help me with that. :)
The author is talking about prefix sum modulo m. So this value must be less than m for all prefix sums. Now there are only m such distinct values possible from 0 to m-1. So if we find modulo for n prefix sums, at least two values must be same.
Thanks sahil23. I got it. :)
Thanks, that was helpful!
Thanks for explanation !
Thanks for the great explanation.
thanks a lot, great help.
This explanation is understandable for everyone.
thanks...
sorry but i didn't understood that part So (Sj — Si) % m = 0. Since Sj — Si = a1+a2+...+Aj — (a1+a2+...+ai) = a(i+1) + ... + aj. So we've got answer.
psum[i] % m = c (c is constant) .......(1)
psum[j] % m = c .......................(2)
subtract eq(1) by eq(2)
(psum[j] — psum[i]) % m = c — c
(psum[j] — psum[i]) % m = 0
this is what we want.
But WHY there is two equal sums modulo M ?
UPD: nicely explained
got it.Thanku balalaika
I did use DP for
n > mactually.With knapsack optimization, you can achieve something like O(M2logN) with pretty small constants.
Submission
I understand your ans is always yes when n > m, pls explain.
if(n > m) //pigeonhole principle { //answer is always yes cout << "YES\n"; return 0; }for n > m, we can calculate prefix sum array, Si = (a0 + a1 + .. + ai ) % m
and always find Si and Sj such that Si % m = Sj % m and j > i.
Since this is always true, there is no need to do all this calculation, and we can directly ouptut YES for n > m.
Why this is always true? Simple: Pigeonhole Principle :)
Very well explained.
Of course, we can use dp in n > m case.
All we have to do is, turn a into [a]m,than count each [ai]m into slots, eg.
turn into
and put number into its slot
We had reduced the prolem into classic 0/1 Knapsack problem with each item's amount greater than 1.
Here is the code, but it would be a little slower:
Actually, we could solve this use Monotone priority queue. in:
see if n>m then when we will process the array a then at every prefix the value of pref[i]%m would be there and there can be at max m distinct values and since n>m there would exist at least (n-m) duplicate values hence the solution would work because if pref[i]%m==x and pref[j]%m==x and j>i; then (pref[j]-pref[i-1])%m=(pref[j]%m-pref[i]%m)==(x-x)==0 hence there would be a subsegment with sum%m==0
Объясните пожалуйста в задаче В второго дивизиона аспект с Дирихле. Как там могут присутствовать две суммы?
Среди любых m+1 чисел от 0 до m-1 неизбежно есть два одинаковых (трудно с этим поспортить), см. также Timus 1032 на эту тему. Поэтому можно отрезать от массива кусок из m+1 чисел и решать задачу на нем.
Это понятно, я знаю Дирихле. Я не могу понять, как там могут присутствовать одинаковые суммы по модулю. К тому же подряд идущих чисел.
Среди чисел a[0], a[0]+a[1], a[0]+a[1]+a[2], ........, a[0]+a[1]+...+a[m] есть два одинаковых, значит их разность (т.е. сумма элементов массива на каком-то отрезке) делится на m. (в разборе именно это и написано, только менее доступными словами)
Все же не могу понять почему есть две одинаковые суммы по модулю M :-(.
UPD: Уже понял, тут ясно написано на английском.
Could someone explain to me Div 1 Problem C? How does the estimate of the length work? I think the worst case sum for the Y direction is 10^6 * 1000 = 10^9. What does "we are spending 1000 to get to the next point of current rectangle and 2000 to get to next rectangle" mean?
Within one rectangle, to jump from one point to other you spend 1000 for X direction but when you jump from one rectangle to another you can spend 2000 as in worst case the points can be 2000 units apart in X direction. So a rough estimate for X direction will be 10^3 * 10^6 + 2000 * 10^3 = 10^9 + 2000000
In total = Ydir + Xdir = 2*10^9 + 2000000
Ahhhh...I used Manhattan minimum spanning tree for solving problem E in Div2, which complexity is O(nlogn) with a big constant. It ran for nearly 2s but I still got AC :)
cool! can you suggest a good article or clip about it ? tanx.
here it is, https://www.topcoder.com/community/data-science/data-science-tutorials/line-sweep-algorithms/
see the last topic
A 2-approximation algorithm for TSP problem when the cost function satisfies the triangle inequality has been mentioned in Introduction to Algorithms. First of all, take a vertex from the graph to be a "root". Then find the MST of the graph and process a DFS from the "root" on the MST. The order you visit all the vertices on the graph will be the same as on the MST. So we just need to get the Manhattan MST using the algorithm mentioned above.
Why did this 2 solutions get TLE in Task C. Div#1 ?!
Sorting vector
Priority Queue
use scanf
My solution for Div.1 C :
Let's call partition(l , r , isVertical , isDescending) recursively and alternate isVertical between 0 and 1. On each call we sort the points from l to r based on isVertical and isDescending, and after that if l < r , we'll call:
partition(l , (l + r)/2 , 1 — isVertical , 0)
partition((l + r)/2 , r , 1 — isVertical , 1)
the first part is sorted in non-decreasing order and the second one in non-increasing order.
Overal complexity : O(nlg^2n)
Can somebody tell why does pow(5,2) returns 24 in the problem Div2 problem C. Here is my solution http://codeforces.me/contest/577/submission/12936883
Because pow(5, 2) returning double, the calculated value will be a little less than 25, and (int) will return the integer part — 24.
Make your own function for this situations.
For problem D there is an Solution
Solution
Edit: Actually its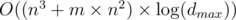
Awesome! Could you describe it in few words?
Sort edges in increasing order of di and add them one by one. After adding each edge i want to know the set of all vertices that we can reach them with using exactly di edges. If we know this set of vertices after adding each edge, we can compute our answer by using BFS every time. Now consider we know a set of vertices S which we can reach them using di - 1 edges and now we want to find all vertices which we can reach them using exactly di edges. Let dp[lvl][i][j] show us is there a path from i to j with exactly 2lvl edges?
If we have this dp we can compute our next set of vertices from set S with an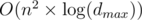 algorithm (I'm not going into details). We do this m times so we get an
algorithm (I'm not going into details). We do this m times so we get an  complexity. The only problem remains is that how we can update dp table after adding one edge. If we add an edge from u to v we should set dp[0][u][v] to true and change some other values on upper levels of dp states. For this we can simply go through higher level and update dp but we stop when we reach some state in dp that was true before (See my dfs function to see what i exactly do). By doing this, each state of dp getting true value at most once and for each time we change something from false to true we do an O(n) iteration. The number of different states is
complexity. The only problem remains is that how we can update dp table after adding one edge. If we add an edge from u to v we should set dp[0][u][v] to true and change some other values on upper levels of dp states. For this we can simply go through higher level and update dp but we stop when we reach some state in dp that was true before (See my dfs function to see what i exactly do). By doing this, each state of dp getting true value at most once and for each time we change something from false to true we do an O(n) iteration. The number of different states is 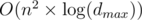 so we get an
so we get an 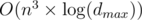 complexity by amortized analyse.
complexity by amortized analyse.
Unless I am mistaken, there is a solution O(n^3*log(dmax)).
I always feel very very happy to have a very very high spped tutorial...
thanks for the editorial....thanks for a good contest....
Can somebody tell why does pow(5,2) returns 24 in problem C Div 2. Here is my solution http://codeforces.me/contest/577/submission/129368833
use ceil(pow(5,2)).
pow(5, 2) doesn't return 24, but it may return something like 24.99999999999
use powl and be safe . it works like pow but without the pains of pow.pow has led me down quite sometimes now :|
But in ideone and other online judges it does return 25, why not in codeforces?
Why you don't use this : (int)(pow(5,2) + 0.5) :D
Edit : the solution had some mistakes , however it passed as a complete search !! :O :'D AC CODE : 12947069
What does "cur" means in your solution ?
May be I got it.idx is the sum,cur is the coin in coin change.
Yes cur means what coin I am adding right now .
I could say your solution is definitely a complete search solution you don't use
arrat all maybe it passed because of weak test data here is your code withoutarr.for div2 problem B
i have solve it using BFS
first of all i take mod m for all in input
and for every value i count how many times it occurs in array
and iterate over all unique values in BFS
state : vis[mod%m][indx of unique value][take]
take mean that i have take a number or not until now
my code : 12947179
That's an elegant solution.
I also thought of similar solution using BFS during the contest but could not come to the conclusion that the total number of states to be visited will fit within time limit.
The total number of states in your solution is 2*1e6. Right? Please correct me if I am wrong.
Yes ,you are right
in the while loop of BFS, you have used the breaking condition.
Why have you included take there? Shouldn't it be just
nope :)
in the first i push to the queue value of mod = 0 ,and this doesn't mean that there is a solution
I see that but doesn't that mean that the number associated with the last state visited(when returning true) should be compulsorily included in the subset?
Nope because the loop inside BFS start from 0 and that mean i didn't take that value
It seems to me that every Div2 B we can solve with BFS. It is very often that exits solution with simple idea, but there are always people who solves it with BFS.
What if they swapped it with C ? As you see problem c is easier than it!
please can you explain what cal() function do
its the BFS function !
tell me what is the thing that you didn't understand and i will explain it :)
these two lines can you explain them
if(indx==int(a.size()) ) continue;
int nxt=(mod + 111*a[indx] *i) m;
a is a vector of unique mod values
when indx == a.size() that mean no any value after that
int(a.size()) : this is for casting unsigned int to signed int
1ll = long long(1) ,(its LL in small case not 11)
i = how many times i will take this value
a[indx] = the value
nxt = next mod after take value[indx] i times
there is o(n) solutoin for div1-c 12947556
I don't sure but maybe your solution is wrong. Let there will be 1000 points in square 1000x1000: 500 in left top corner, 500 in right bottom corner. If two neighbours in path are from different corners distance between them will be from 1500 to 2000. We can fill 1000 squares: a[0][0], a[999][1], a[0][2], a[999][3],.. Distance between two squares is about 1e6. 1e6 * 1000 squares = 1e9. Sum of distances between neighbours in same squares > 1500 * 1000 * 1000 or > 1.5e9. So sum of all distances between neighbours in path > 1e9 + 1.5e9 or > 2.5e9. It's bad. Sorry for bad English.
Actually it's good solution, here is my submission: http://codeforces.me/contest/576/submission/12947556, it is more clear imho. First you clasterize the plane in sqares 1000x1000 and put point respectively in squares that they belong to.
The idea is that you traverse the clasters in a way that there is no distance more than 2000 between any 2 points(1 from first claster,1 from another). Also you can print the points from the same claster in any order because the max distance between any 2 points in a claster is <2500. So if you keep the max distance from any 2 points from the same claster less than 2500 and the distance between any 2 points(different clasters) less than 2500 then the result can not be more than 2500*10^6 or 25*10^8
When you go from one cluster to another, the distance can be up to 3000, so your proof doesn't work.
Yes I found the same case right now. Does the idea work with 800x800 squares?
В Задаче В первого дивизиона, что такое центр дерева?
Вершина, у которой размер каждого поддерева не больше n / 2.
That realy nice problems. Yes, some hard Bdiv2, but its nice CF round, realy new problem from author.
Your idea for Div 2 B was great. Thanks for the awesome problem set.
В задаче C сдалось палево — делил не на 1000, а на 1500 и потом обходил не змейкой, а каждйы раз сверху вниз.
Достигается примерно 109·(4 / 3 + 3 / 2) ≈ 2.8·109
My doubt is, while doing square-root decomposition or similar like in problem DIV2 — E, what is a good interval size to take in similar situation usually, 1.1*root(N) behaves better than root(N). Is 1.2 root(N) better than 1.1*root(N) usually?
DIV2E gave ac if I used interval size = 1100 and no internal sorting whereas WA if I used 1000 as the Interval size.
I have a feeling that any space-filling curve should work well enough for Div. 1 C. For example, Z-order curve suffices to pass the system tests.
Сдал в задаче С разбиение множества пополам между минимальным и максимальным значением по координате по которой разница значений больше. Доказать или опровергнуть не могу..
Аналогично. Умею оценивать 5*10^9. А если один из массивов переворачивать (типа квадродерева буквой П), то будет оценка 4*10^9.
Can anybody squeeze out Div2 E in Python? The best I could get (12948859) runs for about 12.6 seconds on my machine under CPython. Which is weird, since it is essentially parsing + a call to
sort.Can anyone explain Div 1 Problem B in more detail? Why the permutation must have cycle with length 1 or 2?
@malcolm Can you please add editorials to other Div 2 problems?
There is another explanation for div2 B that I couldn't prove, every number we add before we reach m elements there exist some combination that will produce new mod which it didn't appear before thus if n ≥ m there exist a solution. Correct me if I'm wrong.
In Problem A Div.1, If n is not divisible by p^k - 1, do we still need to check with p^k?
For instance, if n is 15, shouldn't the output be
7
2 3 9 5 7 11 13
and not
9
2 4 8 3 9 5 7 11 13 ?
If n is divisible by p^k-1, it doesnt mean that x is.
Could someone explain why checking with the powers of prime is sufficient in Div 2 Problem C ?
If we check with each power of prime <= n, we get the power of that prime in x. If we do this for all primes, we get x.
Problem B Div 1 : Can anyone explain what he means by centers remain unchanged and what he means by applying permutation on the tree?Div#2, Task C:
Input
15
Participant's output
8 2 3 4 5 7 9 11 13
Jury's answer
9 2 4 8 3 9 5 7 11 13
Checker comment
wrong answer cannot distinguish 4 and 8
------------------------------My comment------------------------------ .....Please clarify this ....why we have "8" in expected answer
1) If you ask for 2 and 4 then why 8 ? 2) IF 2 -> NO and 4 -> NO then 8 -> NO IF 2 -> YES and 4 -> NO then 8 -> NO IF 2 -> YES and 4 -> YES then 8 -> YES
so if you can deduct if number is divisible by 9 from asking question "number divisible by 2 & 4"...why "8" is in expected anser
correction in last sentence so if you can deduct if number is divisible by 8 from asking question "number divisible by 2 & 4"...why "8" is in expected anser
4 is divisible by 2,4 but not by 8
Task C. Div1.
How do we decide that we have to divide into 1000 rectangles ?
sqrt(N)
Can you give mathematical/intuitive logic behind taking sqrt(N) ?
Let's split the rows into K buckets so each bucket contains N/K columns . For each bucket sort the numbers by their column number . With processing this order,the total cost coming from the difference between adjacent points' column numbers can be maximum N , so we got a K*N cost. And notice that the difference between adjacent point row numbers' can be maximum N/K, we got an extra N*N/K cost. Total cost is (N*N/K+K*N) to minimize this number we should choose the K as sqrt(N). Note that you should visit first bucket by normal order but the second by reverse order ... I hope it helps :D
I think this contest is inclined to math theory,i dislike :(
I am poor in math , That's exactly why i love this type contests so much for improve myself.
same here
In Div 1 B => It's easy to see that they will turn into each other after applying permutation. That means, all cycles should be even . Can somebody explain this statement ??
Please help with my solution here which timed out
http://codeforces.me/contest/577/submission/12937540
I am doing same thing as (i.e. O(n)) editorial. Moreover by changing few things I optimized it to avoid "/" division by "++" and still my solution go timed out
Please I am not doubting anybody. As per my (biased)knowledge by replacing division operator by ++ in loop, efficiency should have been improved...What am I missing ?...need to learn
Your solution is O(x) while the editorial is O(n)
In your solution it is enough to iterate till sqrt(x) and if i*i=x add 1, else add 2 (ofcourse you should check that both numbers are <=n)
Why this solution 12955987 get WA while this one 12955979 got AC?!
I think the first should get AC too!!!
Why this solution 12955987 get WA while this one 12955979 got AC?!
I think the first should get AC too!!!
in the first code idx can reach up to n which might be 10^6, while your dp array is only 1010*1010
how could idx reach up to 10^6 while i use this condition in the function
and i only call the function if the n < m other wise i cout yes without call the function at all.
Sorry I did not notice that, however your dp state should have a 3rd dimension for cnt
AC Code 12959591
yes that's right. thank you :D
In Problem C Div2, A Div1 Why we just have to ask about prim numbers and its powers while <=n what is the idea here why its enough to guess ?!
because any number n can be written as:
n = a1p1 * a2p2 * ... * ampk
Where ai is prime
why do we need to ask for all powers of a prime like if n = 15 and we divide it with 2 and if the reply is no then we are sure that no powers of this number is going to divide n , but we are asking for 4 and 8 too . why ?
Because you only get a reply after asking all questions, so you can't know that it is not divisible by 2.
Thanks I get it now .
or because. suppose that the reply is yes. you will have to be sure which power of this number is the secret number.
На самом деле, при n = m ответ тоже всегда "YES". Рассмотрим все суммы на префиксах: если не существуют две суммы с одинаковыми остатками, то существует сумма с остатком 0, поскольку всего остатков может быть m (0, 1, ..., m — 1). Если же существуют 2 суммы с одинаковыми остатками, то их разность будет суммой подпоследовательности делящийся на m.
I am trying to Submit DIV2E==DIV1C on Java, but I am getting TL on 6th test, despite the fact that the same solution on C++ got Accepted. I know that there is a problem that Java is pretty slow, but still it seems like my solution does not differs from author's (nlogn) [as far as I know Array.sort works for NlogN, isn't it?]. So is there anything I can do to speed up my solution? Thank you!
The problem is not with the algorithm, but with how you are reading input. Scanner is really slow for reading input. I would suggest using BufferedReader or some fast form of reading input for this problem.
I now used the method, used in fastest solution
But still have the same problem...
Output took a lot of time too. Reading and sorting took together 888 ms. All other time took output. Thank you: AC
Div-1 B / Div-2 D: Can someone explain why there can be at most two centers ?
[and what actually is meant by center]
Is it because the tree will remain disconnected in the other case ?
Centered Tree
thanks ... I now got the underlined graph theory
Can you please explain this => It's easy to see that they will turn into each other after applying permutation. That means, all cycles should be even.
Not necessarily. There could be just one center, in which case there is a fixed point of the permutation.
К сожалению, не смог порешать задачки, пришлось участвовать виртуально :)
Хочется высказать пару слов о задачках.
Когда прочитал Div2-B, я просто завис, думал опять гробовой контест. Но потом почувствовал эффект дежавю, что-то подобное я где-то решал (после того, как исписал пару страниц в попытке найти тест, где n > m и ответ NO, ага)
Div2-C вообще супер-изи. Её очевидно надо было на 2 место ставить.
Очень понравилась задачка D (Div1-B).
Когда прочитал задачку E (Div1-C), подумал, WTF??? и не стал решать. А сегодня с утра придумал очень простое решение (делил на 500, обходил змейкой). Задачка-то намного проще, чем D :)
див 2 Б можно было и без динамики решить. просто перебором, так что норм задача
I got AC in div1 D without any bitwise operation but using the algorithm whose time complexity is O(N^3 log max(d_i)).
here is my code: http://codeforces.me/contest/576/submission/12935207
In this code, I used the following fact: The number of edges don't decrease. We can do doubling efficiently by seeing only the places which are added by each turn.
Объясните кто-нибудь, пожалуйста, что значит "применить перестановку" в задаче Div1B? Просто заместо i вершину обозначить p[i] или что-то другое?
Правильно ли я понял, что "применить перестановку" означает построить граф H изоморфный графу-ответу G? Тогда, предположим, если вершина i в G является центром, то p[i] также является центром в H. Но пока непонятно, из чего следует цикл в перестановке.
Вроде разобрался. Построим граф H изоморфный графу-ответу G. Не сложно проверить, что получится тот же самый граф. Не сложно также проверить, что если вершина i центр дерева G, то p[i] центр дерева H, соответственно p[i] центр G. Если i ≠ p[i], то центра два. Но так как, p[i] обязано перевести в центр, то p[p[i]] = i. Отсюда следует существование цикла.
Am I right?
can someone help me estimating the complexity of this code for Div2-B problem ?
In problem Div 1 A, I was wondering... how about we do binary search for every prime? For example, to find out the biggest power of 2 that divides x for n = 1000, we need 3 questions, not 10. Where is my reasoning wrong?
EDIT: Ignore this question. I hadn't read that he must first ask all the questions before receiving any answer.
It's easy to notice, that centers of that tree must turn into centers after applying the permutation.Why must this be true?
Because if we take the tree and remove all the labels then it must look the same before and after the operation (since all edges are preserved), so all properties of each node that doesn't rely on labels must stay the same. This means that the center nodes must stay the same because you can find them without relying on labels.
how would you find the center without relying on labels? I still don't get this affirmation.
ps: sorry for the necroposting
In task A , DIV 1 ... can anyone please explain to me that for a number X , if X is not divisible by a prime P , then why are we still checking for higher powers of P . For eg if X = 103 , clearly X is not divisible by 3 , but why are we then asking whether X is divisible by 9 or not
Well, you don't know a particular number, you just know that number that you have to guess is less than or equal to N. So, lets say it is 10. Hidden number can be 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10. So lets say Vasya though of number 9. So, if you say 3, the answer is yes, Vasya's number is divisible by 3. But you can't be sure that it is 3 or 9, so you have to ask whether the number is also divisible by 9. That is why you have to check all powers of all the primes.
Can anyone explain why "permutation must have cycle with length 1 or 2 since there're at most two centers. " in Div1B?
Since every center can only connect with node among the centers. Example: when we choose 2, 3, 1 as the centers, connecting (2, 3) will lead to the connection of (3, 1), and then lead to (1, 2), which form a loop.
WTF is 3 centers?
We cannot choose permutation with length greater than 2 as centers, but there can be many centers, consist of those with length 1 or 2.
I want to notice that Div1 D. Flights for Regular Customers task has weak tests. I have just found my accepted solution to be incorrect. I did Dijkstra to test if n-th vertex is reachable after I have added new edges to existing graph when I did enough flights for them.
For the test case below the solution will give 3 instead of correct 2.
4 5
1 1 0
1 2 0
2 3 0
3 4 0
1 4 1
I found other accepted solutions to be wrong as well as mine. One, Two.
Can someone explain Div D (Invariance of Tree) in details?
can anybody explain this very strange submission 22281552?
I solved Div1.A with the lcm of all of pair of numbers, and got AC, but reading editorial I am not very sure about why my code got AC, can anybody explain me?
here's is my code: https://codeforces.me/contest/576/submission/62085651
Div2 B can also be solved with bitsets
Accepted Solution : 80020525
I think the editorial's explanation for Div-2 Problem D/ Div1 Problem B about the necessity of existence cycles of length $$$1$$$ or $$$2$$$ in the permutation is bullshit (some center of tree crap).
Here is the correct proof: First of all I will call permutation cycle as p-cycle.
If p-cycle $$$C1$$$ is connected to cycle $$$C2$$$, then length of $$$C1$$$ must divide length of $$$C2$$$ (we can prove that otherwise, the vertices will form a cycle, hence not a tree).
We can, then, prove that if we interconnect vertices of $$$C2$$$, then we will have a cycle (again easy to prove simple maths).
And if we interconnect vertices of $$$C1$$$, we won't have a cycle, but we will have disconnect component UNLESS the length of cycle is either $$$1$$$ or $$$2$$$.
So there you go :)
Can anyone explain div1/A (div2/C) in more detail ?