Can anyone help with this task.
Given a sequence of N different integers. Operations allowed members of the series are:
Move to the beginning of the sequence
Move to the end of the sequence
Print the smallest number of necessary operations to a default set of ascending sorted.
For example:
Input
4
3 4 2 1
Output
2
Thank you.











We move first 2 on the top
2 3 4 1
And in second move we move 1 on the top.
1 2 3 4
And answer is 2.
And why is it starting from "3 4 2 1" not "4 3 2 1"?
Because sequence in the input is {3,4,2,1}.
You've forgot to tell that in your example first
4is the amount of remaining values, so your statement is bewildering.Usually to get answer you should provide as much clear and correct explanation as possible ;-)
And by the way, what are limitations on input data? This may lead to different solutions...
I think it was quite clear because text said ** different integers** . So with that assumption you could easily understand what is start sequence.
So I'll remember this suggestions for next time.
At first thought answer may be N - LIS where LIS is Longest Increasing Subsequence. LIS can be calculated with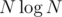 .
.
Doesn't work for case where sequence is {2,4,6,3,8,7}
Answer by N- LIS is 2 , but correct answer is 3.
We have to maximise the set of elements that we don't move. At the end these will all be next to each other, so they have to be a substring of the sorted array, ordered correctly in the original array.
This can be calculated in O(N) by finding, for each position in original array, the longest subsequence of original array ending at that position that is a substring of the sorted array. I think that overall it still must be O(NlogN) because you have to find the sorted array first.