Someday I will arrange C and D correctly :)
I will try to correct mistakes and expand editorial. Russian editorial will be published later.
Firstly, in case c = 0 we should output YES if a = b else answer is NO.
If b belongs to sequence b = a + k * c where k is non-negative integer.
So answer is YES if (b - a) / c is non-negative integer else answer is NO.
x a y
b m c
z d w
Number in the center may be any from 1 to n because number in the center belongs to all subsquares 2 × 2. So, let's find answer with fixed number in the center and then multiply answer by n.
Let's iterate over all possible x. Sums of each subsquare 2 × 2 are the same so x + b + a + m = y + c + a + m and y = x + b - c.
Similarly, z = x + a - d and w = a + y - d = z + b - c.
This square is legal if 1 ≤ y, z, w ≤ n. We should just check it.
Also we can solve this problem in O(1).
We have array ai and should make all numbers in it be equal to zero with minimal number of operations. Sum of all ai equals to zero.
We can divide array into parts of consecutive elements with zero sum. If part has length l we can use all pairs of neighbours in operations and make all numbers be equal to zero with l - 1 operations.
So, if we sum number of operations in each part we get ans = n - k where k is number of parts. We should maximize k to get the optimal answer.
One of the part consists of some prefix and probably some suffix. Each of other parts is subarray of a.
Let's calculate prefix sums. Each part has zero sum so prefix sums before each part-subarray are the same.
So we can calculate f — number of occurencies of the most frequent number in prefix sums and answer will be equal to n - f.
Bonus: how to hack solutions with overflow?
We have binary search tree (BST) and should insert number in it with good time complexity.
Let we should add number x. Find numbers l < x < r which were added earlier, l is maximal possible, r is minimal possible (all will be similar if only one of this numbers exists). We can find them for example with std::set and upper_bound in C++.
We should keep sorted tree traversal (it's property of BST). So x must be right child of vertex with l or left child of vertex with r.
Let l hasn't right child and r hasn't left child. Hence lowest common ancestor (lca) of l and r doesn't equal to l or r. So lca is between l and r in tree traversal. But it's impossible because l is maximal possible and r is minimal possible. So l has right child or r has left child and we know exactly which of them will be parent of x.
That's all. Time complexity is 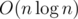 .
.
Let the indexation will be from zero. So we should subtract one from all ai. Also let an - 1 = n - 1.
dpi is sum of shortests pathes from i to i + 1... n - 1.
dpn - 1 = 0
dpi = dpm - (ai - m) + n - i - 1 where m belongs to range from i + 1 to n - 1 and am is maximal. We can find m with segment tree or binary indexed tree or sparse table.
Now answer equals to sum of all dpi.






