| acmsguru |
|---|
| Finished |
→ Problem tags
No tags yet
No tag edit access
The problem statement has recently been changed. View the changes.
×
533. Dice Tower
Time limit per test: 1 second(s)
Memory limit: 262144 kilobytes
Memory limit: 262144 kilobytes
input: standard
output: standard
output: standard
Polycarp loves not only to play games, but to invent ones as well. He has recently been presented with a board game which also had lots of dice. Polycarp quickly noticed an interesting phenomenon: the sum of dots on any two opposite sides equals 7.
The dice
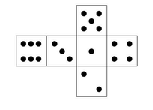
An unfolded die

An example of a tower whose height equals 3
Write a program that would determine the minimum number of dice in the required tower by the given number n. Polycarp can construct any towers whose height equals 1 or more.
Input
The only input line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 106).Output
Print the only integer — the number of dice in the required tower. If no such tower exists, print -1.
Example(s)
sample input | sample output |
50 | 3 |
sample input | sample output |
7 | -1 |
sample input | sample output |
32 | 2 |
Codeforces (c) Copyright 2010-2024 Mike Mirzayanov
The only programming contests Web 2.0 platform
Server time: Nov/22/2024 19:10:26 (h1).
Desktop version, switch to mobile version.
Supported by
User lists

| Name |
|---|




