| acmsguru |
|---|
| Finished |
→ Problem tags
No tags yet
No tag edit access
The problem statement has recently been changed. View the changes.
×
519. 3D City Model
Time limit per test: 0.25 second(s)
Memory limit: 262144 kilobytes
Memory limit: 262144 kilobytes
input: standard
output: standard
output: standard
A city is built on the top of a rectangular n x m grid where all the grid cells are equal squares. Each of the n · m grid cells can serve as a foundation of a single building in the city. A building is represented as a number of 1 x 1 x 1 cubes stacked on the top of each other. The cube that lays in the foundation of a building entirely occupies a single cell on the grid. It is clear that adjacent buildings can share a wall or a part of it. Typical cities can be seen on the image below.
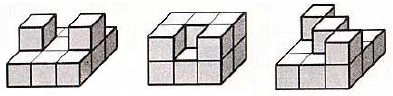
You have to help the King and write a program that will calculate the required surface area of the given model. While calculating the surface area you should count not only the side surfaces, but also the areas of the top and bottom facets.
The model is given to you as n x m matrix of digits. A digit in the j-th position of the i-th row stands for the height of the building with its foundation in cell (i, j) of the model. If the corresponding digit is equal to "
0", it means there is no building built on the top of this cell.
Input
The first line of input contains a pair of integers n, m (1 ≤ n,m ≤ 100), where n — amount of rows in the given grid, m — amount of columns. The following n lines contain the description of the model. These n lines contain m digits each representing heights of the buildings. It's guaranteed that the given matrix contains at least one non-zero digit.Output
Output the only positive integer — surface area of the model.Example(s)
sample input | sample output |
3 3 111 212 111 | 38 |
sample input | sample output |
3 4 1000 0010 0000 | 12 |
Note
The first sample test corresponds to the leftmost picture from the problem statement.Codeforces (c) Copyright 2010-2025 Mike Mirzayanov
The only programming contests Web 2.0 platform
Server time: Feb/19/2025 00:54:50 (i1).
Desktop version, switch to mobile version.
Supported by
User lists

| Name |
|---|




