| acmsguru |
|---|
| Закончено |
→ Теги задачи
Нет тегов
Нет прав на редактирование
Условие задачи было недавно изменено. Просмотреть изменения.
×
455. Sequence analysis
Time limit per test: 1 second(s)
Memory limit: 4096 kilobytes
Memory limit: 4096 kilobytes
input: standard
output: standard
output: standard
Due to the slow 'mod' and 'div' operations with int64 type, all Delphi solutions for the problem 455 (Sequence analysis) run much slower than the same code written in C++ or Java. We do not guarantee that Delphi solution exists.
You are given a sequence of signed 64-bit integers defined as follows:
- x0 = 1,
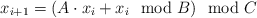 ,
,
modis a remainder operator. All arithmetic operations are evaluated without overflow checking. Use standard "remainder" operator for programming languages (it differs from the mathematical version; for example
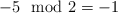 in programming, while
in programming, while 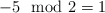 in mathematics). Use "
in mathematics). Use "long long" type in C++, "
long" in Java and "
int64" in Delphi to store xi and all other values.
Let's call a sequence element xp repeatable if it occurs later in the sequence — meaning that there exists such q, q > p, that xq = xp. The first repeatable element M of the sequence is such an element xm that xm is repeatable, and none of the xp where p < m are repeatable.
Given A, B and C, your task is to find the index of the second occurence of the first repeatable element M in the sequence if the index is less or equal to 2 · 106. Per definition, the first element of the sequence has index 0.
Input
The only line of input contains three signed 64-bit integers: A, B and C (B > 0, C > 0).Output
Print a single integer — the index of the second occurence of the first repeatable member if it is less or equal to 2 · 106. Print -1 if the index is more than 2 · 106.Example(s)
sample input | sample output |
2 2 9 | 4 |
sample input | sample output |
2305843009213693951 1 9223372036854775807 | 5 |
sample input | sample output |
-2 1 5 | 4 |
Note
In the first sample test the sequence starts with the following numbers: 1, 3, 7, 6, 3, 7. The first repeatable element is 3. The second occurence of 3 has index 4. In the second sample test the sequence starts with the following numbers: 1, 2305843009213693951, -4611686018427387903, 6917529027641081855, 0, 0, 0. The first repeatable element is 0. The second occurence of 0 has index 5.
In the third sample test the sequence starts with the following numbers: 1, -2, 4, -3, 1, -2, 4. The first repeatable element is 1. The second occurence of 1 has index 4.
Codeforces (c) Copyright 2010-2024 Михаил Мирзаянов
Соревнования по программированию 2.0
Время на сервере: 22.11.2024 19:40:05 (j1).
Десктопная версия, переключиться на мобильную.
При поддержке
Списки пользователей

| Название |
|---|




