You are given a tree (an undirected connected acyclic graph) consisting of $$$n$$$ vertices and $$$n - 1$$$ edges. A number is written on each edge, each number is either $$$0$$$ (let's call such edges $$$0$$$-edges) or $$$1$$$ (those are $$$1$$$-edges).
Let's call an ordered pair of vertices $$$(x, y)$$$ ($$$x \ne y$$$) valid if, while traversing the simple path from $$$x$$$ to $$$y$$$, we never go through a $$$0$$$-edge after going through a $$$1$$$-edge. Your task is to calculate the number of valid pairs in the tree.
The first line contains one integer $$$n$$$ ($$$2 \le n \le 200000$$$) — the number of vertices in the tree.
Then $$$n - 1$$$ lines follow, each denoting an edge of the tree. Each edge is represented by three integers $$$x_i$$$, $$$y_i$$$ and $$$c_i$$$ ($$$1 \le x_i, y_i \le n$$$, $$$0 \le c_i \le 1$$$, $$$x_i \ne y_i$$$) — the vertices connected by this edge and the number written on it, respectively.
It is guaranteed that the given edges form a tree.
Print one integer — the number of valid pairs of vertices.
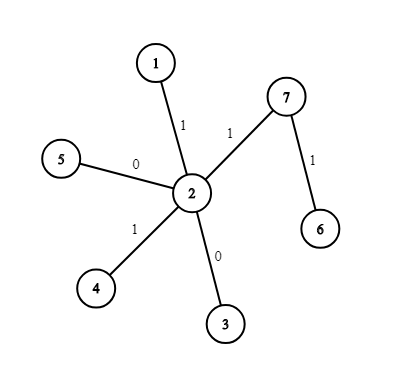
7 2 1 1 3 2 0 4 2 1 5 2 0 6 7 1 7 2 1
34
The picture corresponding to the first example:
| Name |
|---|




