Обновление: разбор G готов
Rayan Programming Contest 2024 - Selection (Codeforces Round 989, Div. 1 + Div. 2)
16:06:33
Зарегистрироваться »
| № | Пользователь | Рейтинг |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | tourist | 3993 |
| 2 | jiangly | 3743 |
| 3 | orzdevinwang | 3707 |
| 4 | Radewoosh | 3627 |
| 5 | jqdai0815 | 3620 |
| 6 | Benq | 3564 |
| 7 | Kevin114514 | 3443 |
| 8 | ksun48 | 3434 |
| 9 | Rewinding | 3397 |
| 10 | Um_nik | 3396 |
| Страны | Города | Организации | Всё → |
| № | Пользователь | Вклад |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | cry | 167 |
| 2 | Um_nik | 163 |
| 3 | maomao90 | 162 |
| 3 | atcoder_official | 162 |
| 5 | adamant | 159 |
| 6 | -is-this-fft- | 158 |
| 7 | awoo | 155 |
| 8 | TheScrasse | 154 |
| 9 | Dominater069 | 153 |
| 10 | djm03178 | 152 |
In this blog I will tell you about recently invented powerful optimization technique, which can be applied to almost any problem and lets you solve it easily. Further I assume that you're already familiar with finding maximum flow in networks. If not, there're many tutorials avaible on Internet. For example, you can read this fabulous article on Topcoder.
It's based on Goldberg-Rao algorithm for finding maximum flow. Its time complexity is 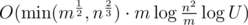 , where U is maximum capacity in network.
, where U is maximum capacity in network.
Consider any network with m edges and n vertices. Any reasonable programmer would merge parallel edges to one edge, summing their capacities, because it obviously reduces running time of algorithm. However, to reduce running time even more, we will not delete parallel edges. Even more, we will add more of them! Let's add parallel edges from sink to source. Obviously, added edges don't affect max flow. But how many edges we need to add? Just enough for m to become more than n2, and the more the better! Now let's look back at time complexity of Goldberg-Rao algorithm. It involves 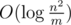 factor, and since we ensured that m > n2, using basic school maths we can prove that this factor is negative. And because all other factors are positive, overall time complexity is negative, which means finding max flow in our network runs in negative time!
factor, and since we ensured that m > n2, using basic school maths we can prove that this factor is negative. And because all other factors are positive, overall time complexity is negative, which means finding max flow in our network runs in negative time!
Let's introduce a subroutine called timelapse, which will every time we call it find max flow in arbitrary network satisfying condition m > n2 using Goldber-Rao algorithm. Since its time complexity is negative, we can win some time once we need it just by calling it!
Now there're some applications of this optimization.
1. Squeezing submissions in time limit.
This one is pretty straight forward. Once running time of your submission is quite close to time limit, you just call timelapse, which gives you some time to finish execution and print calculated answer.
2. Early submit tactic
This one is a bit more tricky. Let's notice that nothing restricts us from having negative running time of the whole submission. So, let's call timelapse a lot of times at the beginning of your code. If you rewind time to the start of the contest, your submission will be accepted at 00:00, which means you can submit all problems you can solve at the first minute of contest and get zero time penalty! Just imagine how unbeateable you will be. However, you have to be careful to not to rewind time too much back. Otherwise your submission will get stuck at 80's when computers were so slow that other part of your code would run for a few years.
Thank you for reading my tutorial. Feel free to discuss this technique in comments and share your ideas and applications of it!
Вот ссылка на простую реализацию вышеописанного решения: http://ideone.com/IoSts1
Шанс, который выпадает раз в жизни! Делайте скриншоты, пока ваш рейтинг больше, чем у Гены!

MikeMirzayanov, fix it, please
В первый раз, когда ты попробуешь СП, ты не почувствуешь никакого кайфа.
Напротив, тебе будет непонятно, почему то, что ты раньше писал наивными способами, теперь надо делать за линию, логарифм или даже единицу. Голова будет болеть и кружится от различных контестов, проводимых везде, где надо и где не надо, ты будешь не понимать, что происходит и зачем ты сюда полез, твоим единственным желанием будет, чтоб ты поскорее вернулся в промышленное программирование.
Именно из-за этого ты, может быть, в следующий раз ты пойдешь на олимпиаду с друзьями, чтоб не ударить в грязь лицом. В этот раз тебе уже не будет так плохо, тебе начнёт казаться, что быть спортивным программистом — круто, и что нет ничего плохого в этом. Тебе будет казаться, что олимпиадный код быстрее и красивее, чем промышленный. Но через пять часов, когда контест закончится, ты почувствуешь острую усталость.
Ты будешь жалеть, что пошел на олимпиаду, от любых оптимизаций, даже выполняемых компилятором, тебя будет мутить — твой мозг будет требовать много чистых Адаптеров, Фабрик и Наблюдателей. Ты, возможно, раз и навсегда завяжешь с СП. Однако после второго контеста тебя будет неутолимо тянуть написать третий. Сильные люди могут сопротивляться этому влечению, однако большинство попробуют и в третий раз.
Третий контест будет такой же тяжёлый, и ты, наверное, захочешь больше никогда не решать олимпиадные задачи, но ты уже не сможешь по-другому. После трёх контестов программист потерян для общества. Ты будешь согласен потратить сколько угодно времени, лишь бы сдать полное решение по гробу. Многие занятые люди станут бросать другие дела, даже жизненно важные, лишь бы получить ещё один АС в свой профиль. Твой код будет выполняться за минимально возможное время и память, но тебе всё равно будет много.
Is there any point in using functional languages (like Haskell, Scala, OCaml) in competitive programming? Yeah, I know that in almost all big competitions they aren't allowed, but, for example, we can use them here on CF. Are there any situations and problems in competitive programming when functional programming would be more preferrable than imperative?
I understand that I'll get downvoted here, but maybe I'll get some help as well. I'm trying to solve 514C using hashing, as it's done in editorial, but why my submission gets WA on test 27?
| Название |
|---|










