Hello everyone,
Recently peltorator created a challenge to create interesting educational blogs. This gave me the motivation to write about a trick I discovered a while back. The trick is simple and I wouldn't be surprised if it already exists with some other name. But I couldn't find any blog on it so I'm making my own.
I have made a data structure that deals with the partition of an array. I call it Cut-Merge-Stick (CMS) trick. A partition of an array is a grouping of its elements into non-empty subarrays, in such a way that every element belongs to exactly one subarray. I refer to every segment in this partition as a "stick".
Some operations on this data structure are merging two consecutive sticks, cutting a single stick into two smaller sticks, getting the longest stick in a range, counting the number of sub-sticks in a range, etc.
Problem statement
You are given a stick of length $$$N$$$ units, placed on the positive $$$X$$$ axis with its left end at the origin. The stick is indexed such that, in between the $$$i$$$-th meter and the $$$i+1$$$-th meter, the number $$$i$$$ is written on the stick, for all $$$0 \le i \le N-1$$$.
You must address $$$Q$$$ queries which will be of the following types:
1 k: Make a cut at $$$x = k$$$ units , As a result, the stick which covers this point is cut into two. It is guaranteed that a cut has not been made at this point prior to the query.2 k: Choose the stick containing the index $$$k$$$. Join it with the stick to its right which is immediately adjacent to it (if such a stick exists).3 k: Print the length of the stick containing the index $$$k$$$.4 l r: Print the length of the longest stick between index $$$l$$$ and index $$$r$$$ (both inclusive). Note that for sticks extending outside the range $$$[l, r]$$$, the length outside the range is not considered.5 l r: Print the number of pairs $$$(i, j)$$$ such that- $$$l \le i \le j \le r$$$
- index $$$i$$$ and index $$$j$$$ are contained in the same stick.
All values in the input are integers. Solve for $$$N, Q \le 2 \cdot 10^5$$$
Preqrequistes
You only need to know about arrays and segment trees. Even the segment tree part can be thought of as a black box with the following points.
Suppose there is an array $$$A$$$ of size $$$N$$$ initially filled with $$$0$$$s. You can assume the following operations/queries are done in $$$O(\log N)$$$ time each.
- Set the value of $$$A_i := A_i + v$$$ for all $$$i$$$ in the range $$$[l, r]$$$
- Get the value of $$$A_l + A_{l+1} + \dots + A_r$$$
- Get the value of $$$\max(A_l, A_{l+1}, \dots, A_r)$$$
If you want to know how the operations can be done then you can refer to the lazy segment tree tutorial in the EDU section.
Idea
Initial setup
For now, let us only focus on the first $$$3$$$ types of queries.
We will denote each stick by consecutive natural numbers starting from $$$1$$$. Let $$$A$$$ be an array of length $$$N$$$ defined as follows. So $$$A_i$$$ will denote the prefix-length of the stick that is at index $$$i$$$. Look at the below picture for a better understanding.
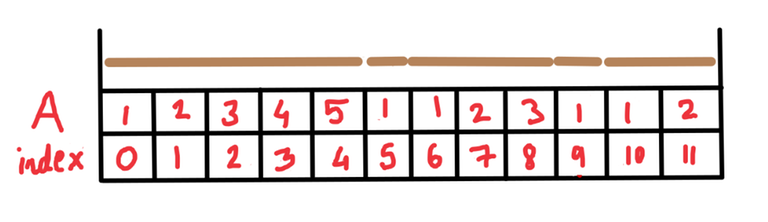
So in this case, the first stick has length $$$5$$$ meters, the second stick has length $$$1$$$ meter, the third stick has length $$$3$$$ meters, the fourth stick has length $$$1$$$ meter and the fifth stick has length $$$2$$$ meters.
Trying the cut operation
Suppose we want to make a cut at $$$x = 2$$$ meters. This will give us $$$2$$$ sticks of length $$$2$$$ and $$$3$$$. The values of $$$A$$$ of the left stick, that is $$$A[0 \dots 1]$$$ are still valid. But for the right stick of length $$$2$$$, that is $$$A[2 \dots 4]$$$, we should re-assign it.
Currently we have $$$A[2 \dots 4] = [3, 4, 5]$$$ but since $$$A[2 \dots 4]$$$ is a new stick we want it to be $$$A[2 \dots 4] = [1, 2, 3]$$$.
We want to add something to $$$A[2...4]$$$ to have it updated correctly.
So $$$X + [3, 4, 5] = [1, 2, 3]$$$
$$$\implies X = [1, 2, 3]- [3, 4, 5] = [-2, -2, -2]$$$
It turns out that If we add $$$-2$$$ to every index in the range $$$[2, 4]$$$ then our array $$$A$$$ will be correctly updated. This is a very useful observation as we can achieve this operation in $$$O(\log N)$$$ time using our black box segment tree.
In general, if we have to make a cut at $$$x=i$$$ meters and the index of the right endpoint of the stick is at $$$r$$$ then we need to do the following to correctly update the array $$$A$$$.
- Let $$$t := A_i$$$
- $$$A_j := A_j + (1 - t)$$$ for all $$$j$$$ in the range $$$[i, r]$$$
Small problem with current cut operation
But not everything is solved yet, how do we get the right-end point of the stick that contains the index $$$i$$$? We can't iterate from left-to-right and check for every index as that takes $$$O(N)$$$ time which is too slow.
Suppose you want to know the index of the left end point of the stick that contains the index $$$i$$$, It is simply the value $$$i -A_i + 1$$$. We can get this value from in $$$O(\log N)$$$ time (because It takes $$$O(\log N)$$$ time to get the value of $$$A_i$$$ from the segment tree).
So we can easily find the left-end point of a stick but we can't find the right-end point? That doesn't sound right, because there is nothing about this problem statement that is special about the left. So the left-side and the right-side should be somewhat symmetric.
Fixing the problem with cut operation
Because of our labeling with the array $$$A$$$ we only get the information about the left-end point for every stick. So, we should just make another array that does the opposite of $$$A$$$. Let us call this array $$$B$$$. So $$$B_i$$$ will hold the suffix length of the stick at index $$$i$$$.
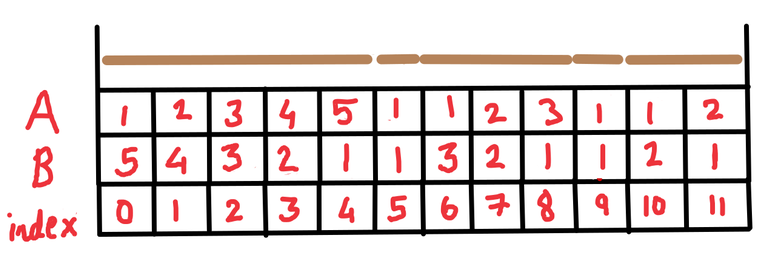
This double-sided labeling turns out to be very useful. Now if we want the left and right endpoints of the stick that contains the index $$$i$$$:
- $$$\text{left endpoint} = i + (1 - A_i)$$$
- $$$\text{right endpoint = } i + (B_i - 1)$$$
- Let us define the function $$$\text{getEndPoints(i) = (left endpoint, right endpoint)}$$$ [pair of left and right end points].
We can get the value of $$$A_i$$$ and $$$B_i$$$ for any $$$i$$$ in $$$O(\log N)$$$ time.
Notice that after cutting at $$$x = 2$$$ meters, the subarray $$$B[2 \dots 4]$$$ will be correctly filled. It is $$$B[0 \dots 1]$$$ that is now incorrect. So to perform the cut operation, we have to update the values in both $$$A$$$ and $$$B$$$.
Before cutting, $$$B[0 \dots 1] = [5, 4]$$$, and after cutting we want it to be $$$B[0 \dots 1] = [2, 1]$$$. Again we observe that $$$[2, 1] - [5, 4] = [-3, -3]$$$
If we add $$$-3$$$ to every index in the range $$$[0, 1]$$$ then our array $$$B$$$ gets updated correctly.
In general if we have to make a cut at $$$x=i$$$ meters and the index of the left endpoint of the stick is at $$$l$$$ then we need to do the following to correctly update the array $$$B$$$.
- Let $$$t := B_{i-1}$$$
- $$$B_j := B_j + (1 -t)$$$ for all $$$j$$$ in the range $$$[l, i-1]$$$
cut operation
So finally, to make a cut at $$$x=i$$$ meters, we have to do the following:
- Let $$$l, r := \text{getEndPoints(i)}$$$
- Let $$$v_A := A_i$$$ and $$$v_B := B_{i-1}$$$
- Set $$$A_j := A_j + (1 - v_A)$$$ for all $$$j$$$ in the range $$$[i, r]$$$
- Set $$$B_j := B_j + (1 - v_B)$$$ for all $$$j$$$ in the range $$$[l, i-1]$$$
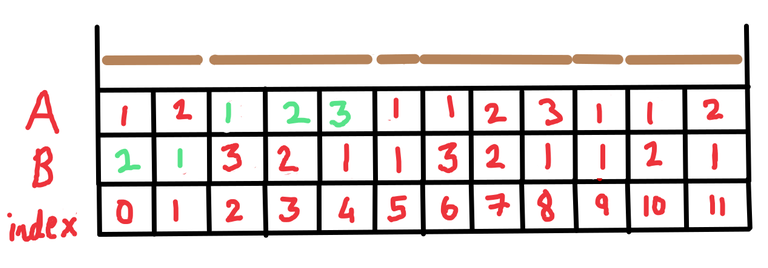
So now the arrays $$$A$$$ and $$$B$$$ look like
Merge operation
Lets say you want to join two consecutive sticks.
To update the values of $$$A$$$, simply add the length of the left stick to each element of $$$A$$$ covered by the right stick. Similarly, to update $$$B$$$, add the length of the right stick to each element of $$$B$$$ covered by the left stick.
- Let $$$l_1, r_1 := \text{getEndPoints(i)}$$$
- Let $$$l_2, r_2 := \text{getEndPoints}(r_1 + 1)$$$
- Set $$$A_j := A_j + (r_1 - l_1 + 1)$$$ for all $$$j$$$ in the range $$$[l_2, r_2]$$$
- Set $$$B_j := B_j + (r_2-l_2+1)$$$ for all $$$j$$$ in the range $$$[l_1, r_1]$$$
It is easy to verify that the updated values of $$$A$$$ and $$$B$$$ become consistent with their definitions
Suppose we perform the merge operation (query of type $$$2$$$) for index $$$9$$$ in the above example. The figure now becomes
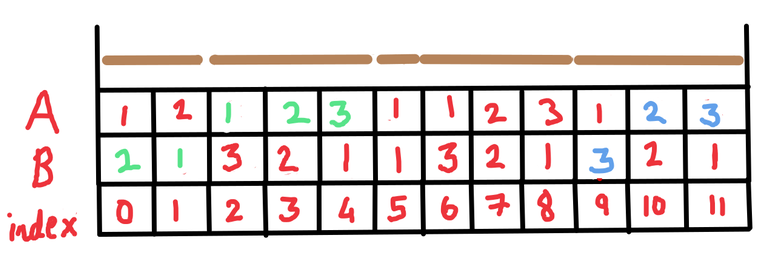
and again perform the merge operation (query of type $$$2$$$) for index $$$7$$$. The figure then becomes
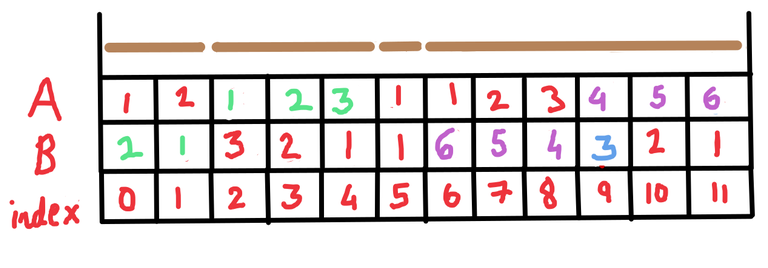
So far we have successfully done queries of type $$$1$$$ and $$$2$$$.
Answering query of type $$$3$$$
The length of the stick containing the index $$$i$$$ $$$= \text{getEndPoints(i).second -getEndPoints(i).first +1}$$$
Answering query of type $$$4$$$
Query of type $$$4$$$ is quite simple. Just do the following:
- Cut at $$$L$$$ meters.
- Cut at $$$R$$$ meters.
- Print the value of $$$\max(A_{L-1}, A_L, \dots, A_{R-1})$$$
- Merge at $$$L-1$$$
- Merge at $$$R-1$$$
Answering query of type $$$5$$$
Query of type 5 is almost exactly the same as type $$$4$$$.
- Cut at $$$L$$$ meters.
- Cut at $$$R$$$ meters.
- Print the value of $$$A_{L-1} + A_L + \dots + A_{R-1}$$$
- Merge at $$$L-1$$$
- Merge at $$$R-1$$$
There are actually too many cut and merge operations that are happening. Although asymptotically it is still $$$O(\log N)$$$ and optimal, in practice, it may slow the program. We can do some case analysis and reduce the number of these function calls. I won't describe them here but they will be implemented in the source code.
Implementation
I have used the AtCoder Library for the implementation of the lazy segment tree required to support range update/query operations. You may want to read the documentation for the lazy segment tree that is used in AtCoder Library.
In the implementation I call the array $$$A$$$ as $$$\text{left_label}$$$ and $$$B$$$ as $$$\text{right_label}$$$.
The implementation has fewer function calls of cut and merge while getting the answer for queries of type $$$3, 4$$$, and $$$5$$$, than what is described above. It is left as an exercise to the reader to figure out these minor optimizations from the implementation (I definitely didn't forget how they work)
Example Problems
ABC217 D Cutting Woods
This is the problem that inspired the trick. This contest was held on Sep 4th 2021. I thought of this trick during the contest, implemented the basics of it and submitted it. During the contest I used a fenwick tree because only range add and point query was needed.
The intended solution of using a std::set<int> never occurred to me during the contest. So I was continuously thinking of compressing the long stick using coordinate compression and solving for the stick of size $$$2\cdot10^5$$$
Once we have the CMS trick the problem is quite easy. We just have to maintain a map that compresses and uncompresses coordinates.
You can refer to my submission here
CF1567E Non-Decreasing Dilemma
I encountered this problem in a rated contest and was shocked. This contest was on Sep 5th, 2021. Exactly $$$1$$$ day after the AtCoder contest, when I thought of this trick. Unfortunately, I had not implemented the code for the full version of this data structure, hence I spent a lot of time debugging bad code that I wrote during the contest.
To solve this problem we realize that a "stick" in this context is a maximal non-decreasing subarray. We can split the given array into disjoint subarrays (partition) such that each subarray is a non-decreasing subarray. Every point update can either cut or merge some sticks.
Instead of doing case analysis to determine if a point update does the cut or merge or both operations, we can explicitly cut at $$$i-1$$$ and $$$i$$$. Perform the point update and then merge at $$$i-1$$$ and $$$i$$$.
You can refer to my submission of the clean version here
Conclusion
I would like to thank Ashishgup, InfernoSloth and JeevanJyot for reviewing/discussing the blog. Special thanks to the_hyp0cr1t3 for many helpful suggestions to improve this blog.
I feel this is a straightforward trick and it solves very specific problems. I had a hard time searching for problems where this trick was applicable. Please post some problems in the comments if the CMS trick can solve them.
I hope this double-sided labeling trick is new to you and you learned something worthwhile. This is my first time writing a tutorial blog, so please leave a comment if I was unclear about something and I will try to clear your doubt. Upvote if you found the blog helpful.
Thank you.
Some Shower Thoughts
- I have used $$$0$$$-based indexing and $$$[l, r]$$$ notation for denoting ranges, as this is my style. But the implementation may be neater if we use $$$1$$$-based indexing and $$$[l, r)$$$ to denote the ranges.
- The capability of this data structure is a subset of the capabilities of a lazy segment tree. The same operations can be achieved using
std::set<int>and/or a generic lazy segment tree in the same time complexity. By generic segment tree I mean, each node holds some information like the size of the subarray, leftmost stick, rightmost stick, etc. Merging $$$2$$$ nodes of the segment tree is not too difficult but it's a pain. As mentioned in the $$$\text{CF 1567E}$$$ problem, the intended code for this alternate implementation is very ugly and laborsome. - I haven't tried any benchmark tests between the CMS trick and the generic segment tree but I'm guessing the CMS trick implementation is faster. Feel free to try your own benchmark tests to prove/disprove my guess.
- It may be possible to merge multiple consecutive sticks in $$$O(\log N)$$$ by lazily merging, but I haven't thought much about it.
- It may be possible to generalize this trick to trees or some other generalization but I have been unsuccessful so far.
- It may be possible to add more functions other than $$$\text{max, min}$$$ but I don't have a deep understanding of the abstractness of lazy propagation in segment trees. I only know that the function $$$f$$$ you apply must satisfy $$$f(ab) = f(a)f(b)$$$ as given in the AtCoder Library documentation.












Well, it's not a trick actually. Just some easy-mid application of segment tree.
Your "CF1567D Non-Decreasing Dilemma" points to 1567 E, not D
fixed, thanks!
I read CMS trick and was dissapointed to see that it is not about finding the tests used in CMS by
sleep(n % (TL / 2));