You have n friends and you want to take m pictures of them. Exactly two of your friends should appear in each picture and no two pictures should contain the same pair of your friends. So if you have n = 3 friends you can take 3 different pictures, each containing a pair of your friends.
Each of your friends has an attractiveness level which is specified by the integer number ai for the i-th friend. You know that the attractiveness of a picture containing the i-th and the j-th friends is equal to the exclusive-or (xor operation) of integers ai and aj.
You want to take pictures in a way that the total sum of attractiveness of your pictures is maximized. You have to calculate this value. Since the result may not fit in a 32-bit integer number, print it modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
The first line of input contains two integers n and m 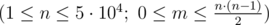 — the number of friends and the number of pictures that you want to take.
— the number of friends and the number of pictures that you want to take.
Next line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the values of attractiveness of the friends.
The only line of output should contain an integer — the optimal total sum of attractiveness of your pictures.
3 1
1 2 3
3
3 2
1 2 3
5
3 3
1 2 3
6
| Name |
|---|




